A Glimpse into the Past: Trends of the 1930s and Their Echoes in 2025
Related Articles: A Glimpse into the Past: Trends of the 1930s and Their Echoes in 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Glimpse into the Past: Trends of the 1930s and Their Echoes in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Glimpse into the Past: Trends of the 1930s and Their Echoes in 2025

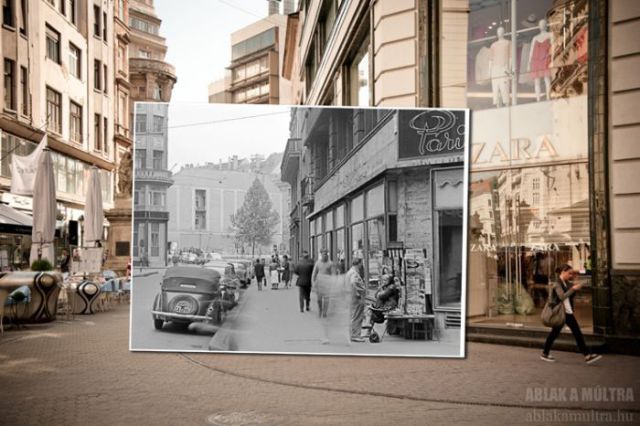
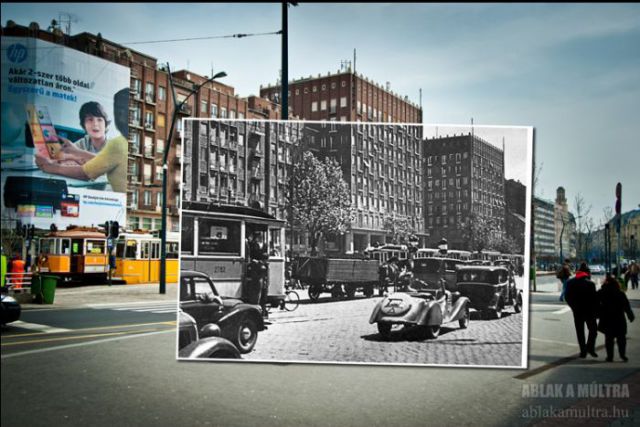
The 1930s, a decade marked by the Great Depression and the rise of fascism, witnessed a confluence of social, economic, and cultural shifts that continue to resonate in the 21st century. While seemingly distant, the trends of this era offer valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities facing us today, particularly in the context of 2025.
Understanding the Echoes of the 1930s in 2025
The echoes of the 1930s are not merely nostalgic reminiscences but rather serve as cautionary tales and potential blueprints for navigating contemporary complexities. The economic hardships, political upheavals, and cultural shifts of the 1930s mirror many of the challenges we face today.
Economic Parallels:
- The Great Depression and the Global Financial Crisis: The Great Depression, a period of unprecedented economic hardship, shares striking parallels with the Global Financial Crisis of 2008. Both events exposed vulnerabilities in global financial systems, leading to widespread unemployment, economic instability, and social unrest.
- The Rise of Protectionism: In response to the Great Depression, many countries implemented protectionist policies, restricting international trade and investment. This trend resurfaced in the 2010s, with the rise of populism and nationalist sentiment leading to increased trade barriers and economic isolationism.
- The Role of Government Intervention: The 1930s saw the rise of government intervention in the economy, with the implementation of New Deal programs in the United States and similar initiatives in other countries. This trend continues today, with governments playing a more active role in regulating markets, providing social safety nets, and stimulating economic growth.
Political Parallels:
- The Rise of Authoritarianism: The 1930s witnessed the rise of authoritarian regimes in Germany, Italy, and Japan, fueled by economic hardship, social unrest, and a desire for strong leadership. The contemporary rise of populist leaders and the erosion of democratic institutions in various parts of the world echo this trend.
- The Erosion of Trust in Institutions: The Great Depression led to a widespread loss of faith in government and financial institutions. Similarly, today, declining trust in political leaders, media outlets, and corporations is a major concern, contributing to social polarization and political instability.
- The Importance of International Cooperation: The 1930s saw a failure of international cooperation, which contributed to the escalation of global conflict. Today, the need for multilateralism and international collaboration is more crucial than ever, particularly in addressing issues like climate change, global pandemics, and economic inequality.
Cultural Parallels:
- The Rise of Pop Culture: The 1930s saw the emergence of popular culture as a powerful force, with movies, radio, and music providing escapism and entertainment during difficult times. This trend continues today, with social media, streaming services, and digital entertainment playing a significant role in shaping cultural trends and influencing public opinion.
- The Importance of Community and Resilience: The Great Depression fostered a sense of community and resilience, as people came together to support each other and overcome adversity. This spirit of community and collective action remains relevant in addressing contemporary challenges, such as climate change, social inequality, and pandemics.
- The Search for Meaning and Purpose: The economic and social upheaval of the 1930s led many individuals to question the meaning of life and seek new forms of spirituality and personal fulfillment. This search for purpose continues today, as individuals navigate complex social and technological landscapes.
Exploring Related Searches:
1. The Great Depression and its Impact on the World
The Great Depression, triggered by the Wall Street Crash of 1929, had a profound impact on economies and societies worldwide. It led to mass unemployment, widespread poverty, and social unrest.
- Economic Impact: The Great Depression led to a sharp decline in global trade, industrial production, and investment. Many businesses went bankrupt, and millions of people lost their jobs.
- Social Impact: The Great Depression led to a rise in homelessness, crime, and social unrest. It also exacerbated existing social inequalities, particularly affecting marginalized communities.
- Political Impact: The Great Depression contributed to the rise of authoritarian regimes in Germany, Italy, and Japan, as people sought strong leadership and economic stability. It also led to the implementation of New Deal programs in the United States, which expanded the role of government in the economy.
2. The Rise of Fascism in the 1930s
Fascism, a totalitarian ideology that emerged in the 1920s and 1930s, gained traction in Europe and Asia during the Great Depression.
- Key Features of Fascism: Fascism is characterized by its emphasis on nationalism, militarism, and authoritarianism. It rejects liberal democracy and individual rights, promoting a strong state and a single leader.
- Causes of Fascism: The Great Depression created a climate of economic hardship and social unrest, which made people receptive to fascist ideas. Fascism offered a promise of strong leadership, economic recovery, and national unity.
- Consequences of Fascism: The rise of fascism led to the outbreak of World War II, resulting in millions of deaths and widespread destruction. It also had a lasting impact on global politics and society.
3. The New Deal and its Legacy
The New Deal, a series of programs and reforms implemented by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States during the Great Depression, aimed to provide economic relief, stimulate recovery, and reform the financial system.
- Key Programs of the New Deal: The New Deal included programs such as the Social Security Act, the Works Progress Administration, and the Tennessee Valley Authority. These programs provided jobs, social security, and public infrastructure projects.
- Impact of the New Deal: The New Deal helped to mitigate the worst effects of the Great Depression and created a more robust social safety net. It also expanded the role of government in the economy and led to the establishment of key regulatory agencies.
- Legacy of the New Deal: The New Deal had a lasting impact on American society, laying the foundation for the modern welfare state. Its principles continue to influence government policies today, particularly in areas such as social security, unemployment insurance, and public infrastructure.
4. The 1930s and the Rise of Modernism
The 1930s saw a flowering of artistic and intellectual creativity, with the emergence of modernism in art, literature, music, and architecture.
- Key Features of Modernism: Modernism rejected traditional forms and conventions, embracing experimentation, innovation, and a focus on individual expression.
- Influence of the 1930s on Modernism: The economic hardship and social unrest of the 1930s influenced modern art, literature, and music, with artists seeking to express the anxieties, struggles, and aspirations of the time.
- Legacy of Modernism: Modernism had a profound impact on artistic and cultural trends, shaping the development of art, literature, and music in the 20th and 21st centuries.
5. The 1930s and the Rise of Consumer Culture
Despite the Great Depression, the 1930s saw the emergence of consumer culture, with the rise of mass production, advertising, and new products.
- The Impact of Mass Production: The development of mass production techniques led to the availability of consumer goods at lower prices, making them accessible to a wider range of people.
- The Role of Advertising: Advertising played a key role in promoting consumerism, creating demand for new products and shaping consumer preferences.
- The Rise of Department Stores: Department stores became popular destinations for shopping, offering a wide range of goods under one roof.
6. The 1930s and the Role of Women
The 1930s saw a shift in the role of women in society, with women taking on new responsibilities and challenging traditional gender roles.
- Women in the Workforce: During the Great Depression, women entered the workforce in increasing numbers, filling jobs previously held by men.
- Women in Politics and Activism: Women also became more active in politics and social activism, advocating for women’s rights, social justice, and economic equality.
- The Changing Image of Women: The 1930s saw a shift in the image of women in popular culture, with women being portrayed as more independent and assertive.
7. The 1930s and the Rise of Technology
The 1930s saw significant technological advancements, particularly in the areas of transportation, communication, and entertainment.
- The Development of the Automobile: The automobile continued to gain popularity, transforming transportation and contributing to the growth of suburbs.
- The Rise of Radio: Radio broadcasting became widespread, providing entertainment, news, and information to millions of people.
- The Development of Motion Pictures: Motion pictures continued to evolve, with the introduction of sound and color, enhancing the cinematic experience.
8. The 1930s and the Shaping of the 21st Century
The trends of the 1930s have had a lasting impact on the world, shaping the social, economic, and political landscape of the 21st century.
- The Importance of Economic Stability: The Great Depression highlighted the importance of economic stability and the need for government intervention to prevent future crises.
- The Need for International Cooperation: The failure of international cooperation in the 1930s underscores the importance of multilateralism and global cooperation in addressing contemporary challenges.
- The Importance of Social Justice: The social inequalities exacerbated by the Great Depression continue to be a concern today, highlighting the need for social justice and economic equality.
FAQs: Trends of the 1930s and Their Echoes in 2025
1. How did the Great Depression impact the world?
The Great Depression had a profound impact on the world, leading to widespread economic hardship, social unrest, and political instability. It triggered a decline in global trade, industrial production, and investment, resulting in mass unemployment, poverty, and homelessness. The economic crisis also contributed to the rise of authoritarian regimes in Germany, Italy, and Japan, as people sought strong leadership and economic stability.
2. What are the parallels between the Great Depression and the Global Financial Crisis of 2008?
Both events exposed vulnerabilities in global financial systems, leading to widespread unemployment, economic instability, and social unrest. Both crises highlighted the interconnectedness of global economies and the need for regulatory mechanisms to prevent future financial meltdowns.
3. How does the rise of populism and nationalism echo the trends of the 1930s?
The rise of populist leaders and the erosion of democratic institutions in various parts of the world echo the trend of authoritarianism that emerged in the 1930s. Both phenomena are fueled by economic hardship, social unrest, and a desire for strong leadership. Populist leaders often appeal to nationalist sentiments and exploit anxieties about economic insecurity and cultural change, mirroring the tactics employed by fascist leaders in the 1930s.
4. What are the lessons learned from the 1930s that are relevant to today’s world?
The 1930s offer valuable lessons about the importance of economic stability, international cooperation, and social justice. The Great Depression highlighted the need for government intervention to prevent future economic crises and the importance of robust social safety nets. The failure of international cooperation in the 1930s underscores the need for multilateralism and global collaboration in addressing contemporary challenges such as climate change, global pandemics, and economic inequality. The social inequalities exacerbated by the Great Depression continue to be a concern today, highlighting the need for social justice and economic equality.
5. How do cultural trends of the 1930s resonate with the contemporary world?
The 1930s saw the emergence of popular culture as a powerful force, with movies, radio, and music providing escapism and entertainment during difficult times. This trend continues today, with social media, streaming services, and digital entertainment playing a significant role in shaping cultural trends and influencing public opinion. The search for meaning and purpose that characterized the 1930s also resonates with contemporary society, as individuals navigate complex social and technological landscapes.
Tips for Navigating the Echoes of the 1930s in 2025
- Embrace International Cooperation: The 1930s demonstrated the dangers of isolationism and the importance of international collaboration. In today’s interconnected world, addressing global challenges like climate change, pandemics, and economic inequality requires strong multilateralism and coordinated action.
- Strengthen Democratic Institutions: The erosion of trust in institutions and the rise of authoritarianism are serious concerns. Protecting democratic values, promoting transparency and accountability, and fostering civic engagement are crucial for maintaining a stable and just society.
- Foster a Sense of Community: The 1930s showed the resilience and strength of communities in times of crisis. Building a sense of shared purpose and supporting vulnerable populations are essential for navigating challenges and fostering social cohesion.
- Embrace Innovation and Creativity: The 1930s saw a flourishing of artistic and intellectual creativity, even in the face of hardship. Embracing innovation, fostering creativity, and supporting the arts are essential for economic growth, social progress, and cultural enrichment.
Conclusion
The trends of the 1930s, though seemingly distant, offer valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities facing us today. By understanding the echoes of this era in the context of 2025, we can better navigate the complexities of our time, drawing lessons from the past to inform our present and shape a brighter future. The 1930s serve as a reminder that economic hardship, political instability, and cultural shifts are not unique to any particular era. Instead, they are recurring themes in human history, demanding our attention and our collective action. By learning from the past, we can build a more resilient, equitable, and sustainable future for all.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Glimpse into the Past: Trends of the 1930s and Their Echoes in 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!