Agriculture Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Food Production
Related Articles: Agriculture Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Food Production
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Agriculture Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Food Production. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Agriculture Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Food Production
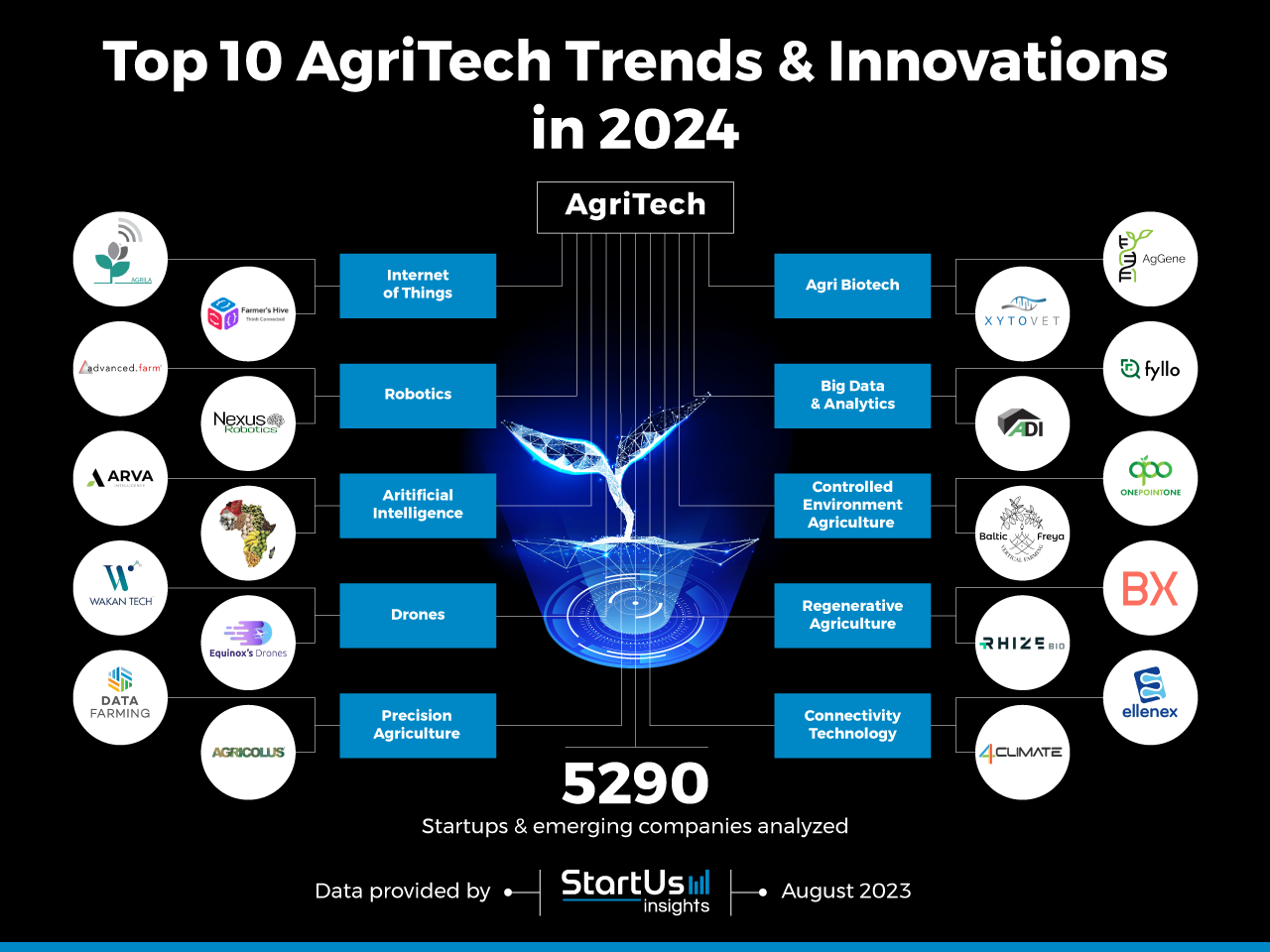
The world’s population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050, placing immense pressure on food production systems. To meet this growing demand, the agricultural industry must adapt and innovate. Agriculture trends 2025 are not merely predictions; they are the roadmap to ensuring food security and sustainability for future generations. These trends are driven by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and evolving consumer preferences.
This comprehensive exploration delves into the key trends shaping the future of agriculture, examining their potential impact and highlighting the crucial role they play in transforming the global food system.
1. Precision Agriculture: Data-Driven Decision Making
Precision agriculture leverages technology to optimize farming practices, maximizing yields and minimizing resource use. This approach involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources, including sensors, drones, satellites, and weather stations.
- Data Analytics: Data analysis helps farmers understand crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
- Variable-Rate Technology: This technology allows farmers to apply inputs like fertilizer and pesticides precisely where needed, reducing waste and environmental impact.
- Remote Sensing: Drones and satellites provide real-time insights into crop growth and health, facilitating timely intervention and efficient resource allocation.
Benefits of Precision Agriculture:
- Increased Productivity: Optimized resource management leads to higher yields and improved farm profitability.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Minimized use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides contributes to environmental sustainability.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automated processes and data-driven decision-making streamline farm operations.
2. Vertical Farming: Growing Up, Not Out
Vertical farming involves cultivating crops in stacked layers, maximizing space utilization and minimizing land requirements. This innovative approach is particularly relevant in urban areas where land is scarce.
- Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA): Vertical farms utilize controlled environments to optimize growing conditions, ensuring consistent yields and high-quality produce.
- Hydroponics, Aeroponics, and Aquaponics: These techniques utilize water-based systems for growing crops, eliminating soil-borne diseases and reducing water usage.
- Urban Agriculture: Vertical farms offer a solution for urban food production, reducing reliance on long-distance transportation and supporting local food systems.
Benefits of Vertical Farming:
- Increased Productivity: High-density cultivation allows for significant yield increases in limited space.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Minimized water usage, reduced pesticide use, and localized production contribute to sustainability.
- Enhanced Food Security: Provides a reliable source of fresh produce in urban areas, enhancing food accessibility.
3. Sustainable Agriculture: Protecting the Environment
Sustainable agriculture focuses on practices that minimize environmental impact, conserve natural resources, and promote biodiversity. This approach emphasizes long-term sustainability, ensuring food production for future generations.
- Organic Farming: Organic farming prohibits the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, promoting soil health and biodiversity.
- Agroecology: This approach integrates ecological principles into farm management, fostering ecosystem services and enhancing soil fertility.
- Regenerative Agriculture: Regenerative practices aim to improve soil health, sequester carbon, and enhance biodiversity, contributing to climate change mitigation.
Benefits of Sustainable Agriculture:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Sustainable practices contribute to mitigating climate change by reducing carbon footprint.
- Enhanced Biodiversity: Protecting and promoting biodiversity ensures ecosystem resilience and healthy food systems.
- Improved Soil Health: Healthy soils are crucial for sustainable food production, providing nutrients and supporting biodiversity.
4. Gene Editing and Bioengineering: Enhancing Crop Traits
Gene editing and bioengineering technologies allow for targeted modifications to crop genomes, enhancing desirable traits such as yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content.
- CRISPR-Cas9 Technology: This gene editing technique allows for precise alterations in plant genomes, accelerating crop improvement.
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs): GMOs are crops with modified genes, often conferring traits like pest resistance or herbicide tolerance.
- Biofortification: Bioengineering techniques can enhance the nutritional content of crops, addressing micronutrient deficiencies in vulnerable populations.
Benefits of Gene Editing and Bioengineering:
- Increased Yield and Quality: Improved crop traits can lead to higher yields and better quality produce.
- Enhanced Nutrient Content: Biofortification can improve the nutritional value of crops, addressing malnutrition.
- Reduced Pesticide Use: Pest-resistant crops can minimize the need for chemical pesticides, reducing environmental impact.
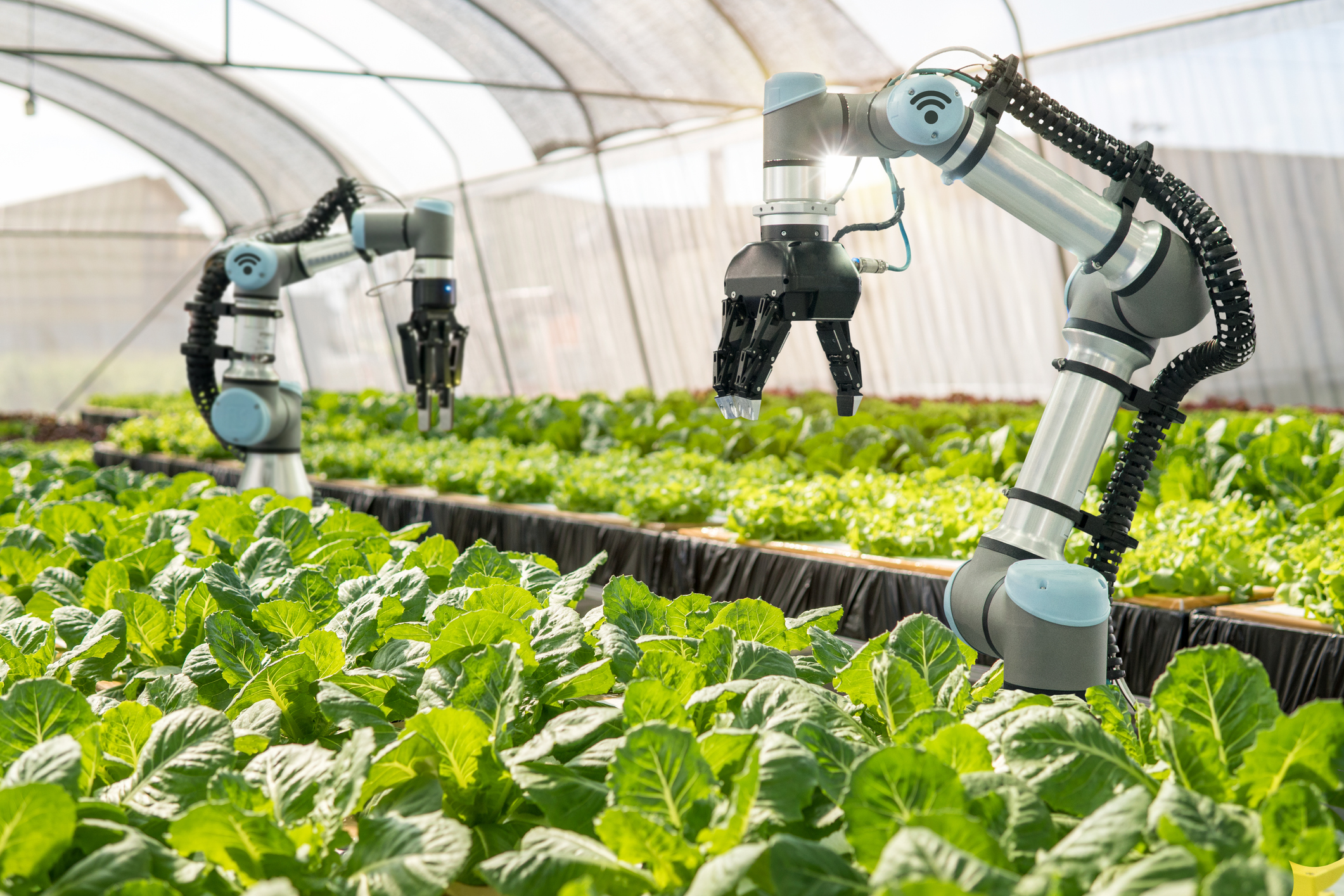
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Optimizing Farm Management
AI is transforming the agricultural industry by providing insights, automating tasks, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can analyze data to predict crop yields, weather patterns, and potential disease outbreaks.
- Robotics and Automation: Robots and autonomous vehicles can perform tasks like planting, harvesting, and weeding, enhancing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
- Precision Livestock Management: AI can monitor livestock health and behavior, optimizing feeding and disease prevention strategies.
Benefits of AI in Agriculture:
- Increased Efficiency: AI-powered automation streamlines farm operations and reduces labor requirements.
- Improved Decision Making: AI algorithms provide data-driven insights, enabling farmers to make informed decisions.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Optimized resource allocation and disease prevention strategies contribute to environmental sustainability.
6. Blockchain Technology: Enhancing Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent platform for tracking food products from farm to fork. This enhances traceability and accountability, building trust in the food supply chain.
- Food Safety and Quality Control: Blockchain records provide a comprehensive history of food products, enabling rapid identification and response in case of contamination.
- Fair Trade and Ethical Sourcing: Blockchain technology can track the origin of food products, ensuring fair compensation for farmers and ethical sourcing practices.
- Consumer Information and Choice: Consumers can access information about the origin, production methods, and sustainability of food products.
Benefits of Blockchain in Agriculture:
- Enhanced Transparency and Traceability: Blockchain provides a secure and immutable record of food products, increasing transparency and accountability.
- Improved Food Safety: Rapid identification of contaminated products and enhanced traceability contribute to food safety.
- Increased Consumer Trust: Transparency in the food supply chain builds consumer trust and confidence in the products they consume.
7. Alternative Protein Sources: Expanding Dietary Options
The growing demand for protein is driving the exploration of alternative protein sources beyond traditional animal-based options.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Legumes, nuts, seeds, and soy products offer sustainable and nutritious protein alternatives.
- Insect Protein: Insects are a highly efficient protein source with a low environmental footprint.
- Cellular Agriculture: Cultured meat and other protein sources grown in labs offer a sustainable and ethical alternative to animal-based protein.
Benefits of Alternative Protein Sources:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Plant-based and insect protein sources have a lower environmental footprint compared to animal agriculture.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Alternative protein sources contribute to sustainable food systems by reducing reliance on traditional livestock production.
- Expanded Dietary Options: Offers diverse and nutritious protein choices for consumers with various dietary preferences.
8. Consumer-Driven Trends: Demand for Healthy, Ethical, and Sustainable Food
Consumer preferences are evolving, driving demand for healthy, ethical, and sustainable food products.
- Organic and Natural Foods: Consumers increasingly seek food products grown without synthetic pesticides and fertilizers.
- Local and Regional Sourcing: Supporting local farmers and reducing food miles are becoming increasingly important to consumers.
- Ethical and Sustainable Production Practices: Consumers are demanding transparency and accountability in food production, including animal welfare and environmental sustainability.
Benefits of Consumer-Driven Trends:
- Increased Demand for Sustainable Practices: Consumer preferences drive innovation and adoption of sustainable agricultural practices.
- Support for Local Food Systems: Consumer demand for local produce fosters the development of regional food systems.
- Improved Food Quality and Safety: Consumer awareness and demand for ethical and sustainable food practices enhance food quality and safety.
Related Searches
- Future of Agriculture: This search explores long-term trends and predictions for the agricultural industry, including technological advancements, environmental challenges, and societal shifts.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: This search focuses on methods and strategies for environmentally friendly and resource-efficient agriculture, including organic farming, agroecology, and regenerative agriculture.
- Precision Agriculture Technology: This search delves into specific technologies used in precision agriculture, such as sensors, drones, data analytics, and variable-rate application systems.
- Vertical Farming Systems: This search investigates various vertical farming techniques, including hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics, and their potential for urban agriculture.
- Gene Editing in Agriculture: This search explores the use of gene editing technologies, particularly CRISPR-Cas9, in crop improvement and enhancing desirable traits.
- Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture: This search examines the application of AI in agriculture, including predictive analytics, robotics, and precision livestock management.
- Blockchain in Food Supply Chain: This search focuses on the role of blockchain technology in enhancing transparency, traceability, and food safety in the food supply chain.
- Alternative Protein Sources: This search investigates various alternative protein sources, including plant-based proteins, insect protein, and cellular agriculture, and their potential to meet growing protein demand.
FAQs about Agriculture Trends 2025
1. How will these trends impact food security?
Agriculture trends 2025 are crucial for ensuring food security in a world facing a rapidly growing population and climate change. Technological advancements, such as precision agriculture and vertical farming, will enhance productivity and resource efficiency. Sustainable practices will protect the environment and ensure long-term food production. Alternative protein sources will expand dietary options and reduce reliance on traditional animal agriculture.
2. What are the challenges associated with these trends?
While these trends offer promising solutions, they also present challenges. Implementing precision agriculture requires significant investments in technology and data infrastructure. Vertical farming faces limitations in scaling up and requires significant energy consumption. Sustainable agriculture requires a shift in farming practices and consumer behavior. Gene editing and bioengineering raise ethical concerns and regulatory challenges.
3. How can consumers contribute to these trends?
Consumers play a crucial role in driving the adoption of agriculture trends 2025. By choosing organic and sustainably produced food products, supporting local farmers, and embracing alternative protein sources, consumers can create demand for sustainable and innovative agricultural practices.
4. What are the future implications of these trends?
Agriculture trends 2025 will reshape the global food system, leading to more efficient, sustainable, and resilient food production. The integration of technology, sustainable practices, and consumer preferences will transform the way we grow, distribute, and consume food.
Tips for Adapting to Agriculture Trends 2025
- Embrace Technology: Invest in data analytics, precision farming tools, and AI-powered solutions to enhance efficiency and decision-making.
- Adopt Sustainable Practices: Implement organic farming, agroecology, and regenerative agriculture principles to minimize environmental impact and enhance soil health.
- Explore Alternative Protein Sources: Investigate plant-based proteins, insect protein, and cellular agriculture to diversify protein sources and reduce reliance on traditional livestock.
- Engage with Consumers: Communicate transparently about your farming practices and the sustainability of your products to build consumer trust and loyalty.
- Collaborate and Network: Connect with other farmers, researchers, and industry experts to share knowledge and learn about innovative solutions.
Conclusion
Agriculture trends 2025 represent a paradigm shift in food production, driven by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and evolving consumer preferences. These trends offer promising solutions to the challenges of feeding a growing global population while protecting the environment. By embracing innovation, adopting sustainable practices, and engaging with consumers, the agricultural industry can shape a future of food security, sustainability, and resilience.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Agriculture Trends 2025: Shaping the Future of Food Production. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
