Navigating the Future of Energy: Trends Shaping the Landscape in 2025
Related Articles: Navigating the Future of Energy: Trends Shaping the Landscape in 2025
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Future of Energy: Trends Shaping the Landscape in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Future of Energy: Trends Shaping the Landscape in 2025

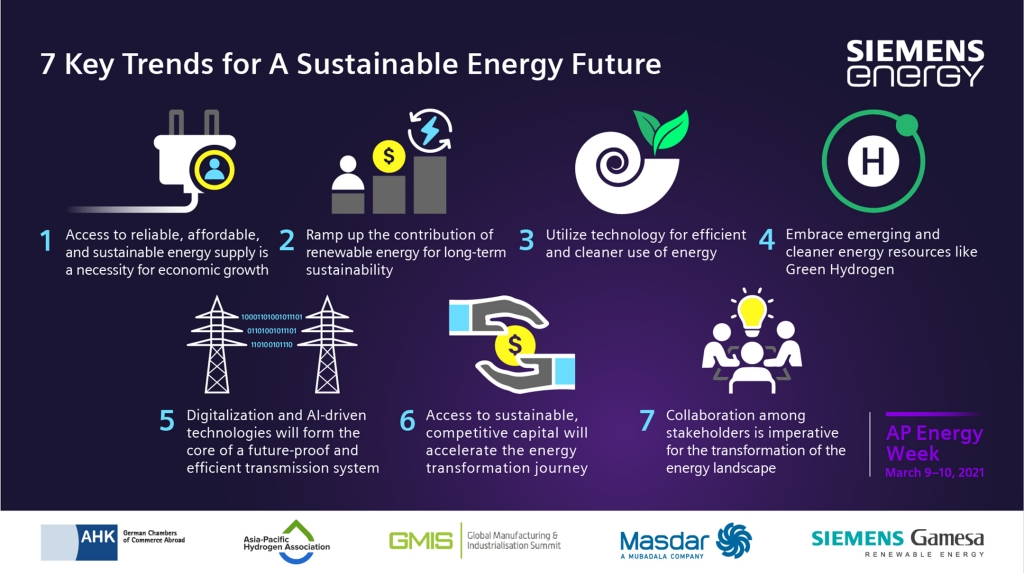
The energy sector is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and a growing awareness of climate change. As we approach 2025, several key trends are shaping the energy landscape, promising a future that is cleaner, more efficient, and more resilient. This article delves into these trends, exploring their implications and the opportunities they present.
1. The Rise of Renewables:
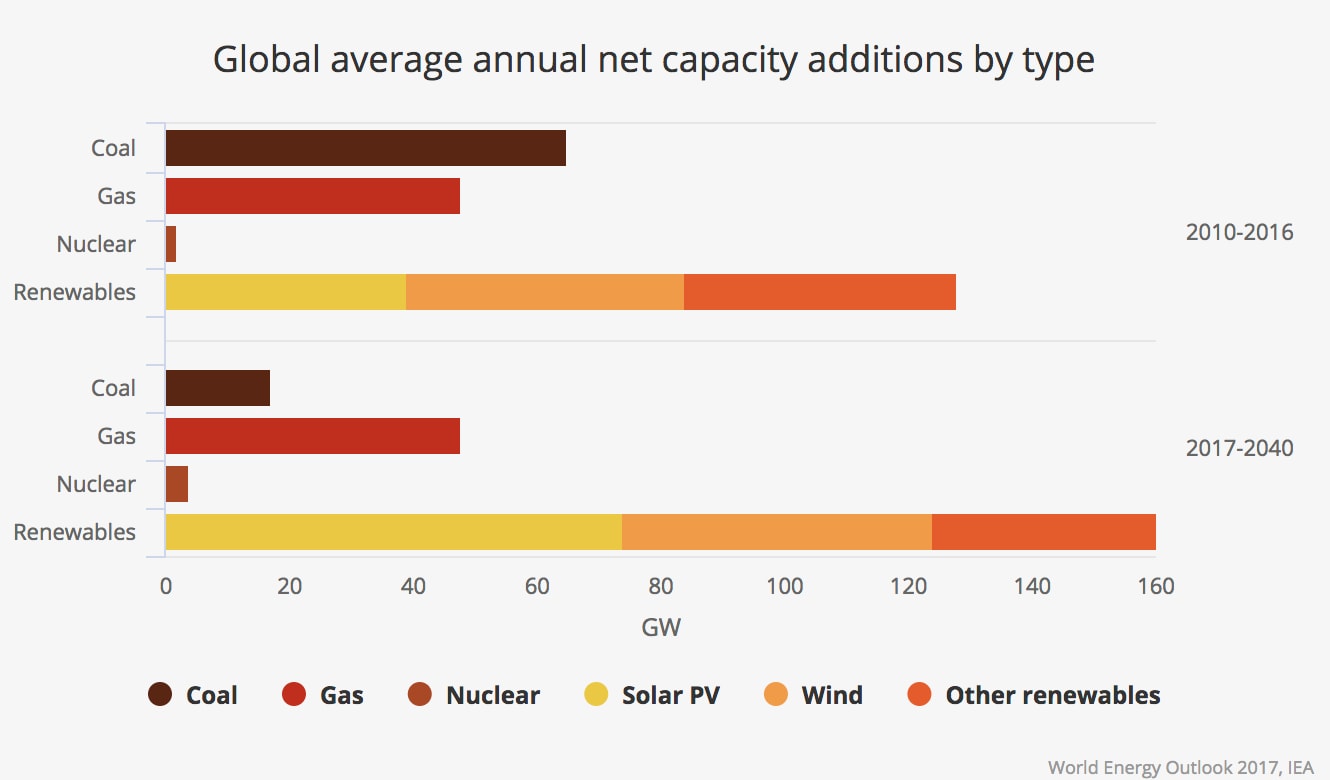
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro, are experiencing unprecedented growth. Driven by falling costs and increasing policy support, renewables are poised to become the dominant source of electricity generation in many parts of the world by 2025.
- Solar Energy: Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology has become increasingly efficient and affordable, making it a viable option for residential, commercial, and utility-scale installations. The global solar PV market is expected to grow significantly, with solar energy playing a crucial role in achieving decarbonization goals.
- Wind Energy: Onshore and offshore wind power are experiencing rapid expansion, driven by technological advancements in turbine design and improved grid integration. Wind energy is particularly attractive for its scalability and ability to generate electricity on a large scale.
- Hydropower: Hydroelectric power remains a significant source of renewable energy, particularly in regions with abundant water resources. New developments in pumped hydro storage are enhancing the reliability and flexibility of hydropower, making it a valuable asset in balancing the grid.
2. Decentralized Energy Systems:
The rise of distributed generation and energy storage technologies is leading to a shift towards more decentralized energy systems. This trend is driven by factors such as:
- Increased Consumer Demand for Control: Consumers are increasingly interested in having greater control over their energy consumption and production.
- Growing Availability of Renewable Energy Sources: The proliferation of rooftop solar panels and small-scale wind turbines is enabling households and businesses to generate their own electricity.
- Advancements in Battery Storage: Battery storage technologies are becoming more affordable and efficient, allowing for the storage and management of renewable energy, making it more reliable.
Decentralized energy systems offer numerous benefits, including increased energy security, reduced reliance on centralized grids, and lower emissions.
3. Smart Grid Technologies:
Smart grids are essential for integrating renewable energy sources and managing the increasing complexity of energy systems. These advanced grids utilize digital technologies to enhance grid reliability, efficiency, and responsiveness.
- Real-time Monitoring and Control: Smart grids enable real-time monitoring of energy flows, allowing for efficient dispatch of generation and demand management.
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): AMI allows for two-way communication between utilities and consumers, providing real-time data on energy consumption and enabling demand response programs.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DER) Integration: Smart grids can integrate distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar panels and battery storage, into the grid, optimizing energy flows and enhancing grid resilience.
4. Hydrogen Energy:
Hydrogen is gaining traction as a clean fuel source, particularly for transportation and industrial applications. Hydrogen can be produced through electrolysis using renewable electricity, making it a potential solution for decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors.
- Fuel Cells: Fuel cells convert hydrogen into electricity with high efficiency and zero emissions. They are being deployed in a variety of applications, including transportation, stationary power generation, and industrial processes.
- Hydrogen Storage and Distribution: Advancements in hydrogen storage and distribution technologies are crucial for scaling up hydrogen production and deployment.
- Green Hydrogen: Green hydrogen produced from renewable energy sources offers a truly sustainable solution for decarbonization.
5. Energy Efficiency and Conservation:
Energy efficiency remains a crucial aspect of the energy transition. Reducing energy consumption through improved technologies, behavioral changes, and policy interventions is essential for achieving sustainability goals.
- Building Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient building codes and standards, utilizing smart building technologies, and promoting energy audits can significantly reduce energy consumption in buildings.
- Industrial Efficiency: Technological advancements and process optimization can improve energy efficiency in industrial processes, reducing emissions and lowering operating costs.
- Transportation Efficiency: Electric vehicles, fuel-efficient engines, and smart transportation systems are contributing to a more efficient transportation sector.
6. Digitalization and Data Analytics:
Digital technologies are transforming the energy sector, enabling better data collection, analysis, and decision-making.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices are being deployed across the energy value chain, providing real-time data on energy consumption, production, and grid performance.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are being used for predictive maintenance, grid optimization, and demand forecasting, improving efficiency and reliability.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can enhance energy trading and accounting transparency, enabling peer-to-peer energy transactions and facilitating the integration of distributed energy resources.
7. Energy Storage:
Energy storage technologies are essential for integrating variable renewable energy sources, balancing supply and demand, and enhancing grid reliability.
- Battery Storage: Battery storage is becoming increasingly affordable and efficient, making it a viable option for residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications.
- Pumped Hydro Storage: Pumped hydro storage remains a significant energy storage option, particularly in regions with suitable topography.
- Other Storage Technologies: Other emerging storage technologies, such as compressed air energy storage (CAES) and thermal energy storage, are also gaining traction.
8. Energy Policy and Regulation:
Governments around the world are implementing policies and regulations to promote the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy system.
- Renewable Energy Targets: Many countries have set ambitious renewable energy targets, providing incentives for renewable energy development and deployment.
- Carbon Pricing: Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems, are being implemented to encourage emissions reductions.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Energy efficiency standards for buildings, appliances, and vehicles are being strengthened to reduce energy consumption.
Related Searches:
- Energy Trends 2025: This search term reflects a broad interest in the overall energy landscape in 2025.
- Future of Energy: This search term explores the long-term outlook for the energy sector, including technological advancements, policy shifts, and societal changes.
- Renewable Energy Trends: This search term focuses specifically on the growth and development of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower.
- Energy Storage Technologies: This search term delves into the various technologies being developed for energy storage, including batteries, pumped hydro, and compressed air energy storage.
- Smart Grids: This search term explores the role of smart grids in integrating renewable energy, managing demand, and enhancing grid reliability.
- Decentralized Energy: This search term focuses on the trend towards distributed generation and energy storage, enabling greater consumer control and reducing reliance on centralized grids.
- Energy Efficiency: This search term highlights the importance of reducing energy consumption through technological advancements, behavioral changes, and policy interventions.
- Hydrogen Energy: This search term explores the potential of hydrogen as a clean fuel source, particularly for transportation and industrial applications.
FAQs:
-
What are the biggest challenges facing the energy transition?
- Cost of Renewable Energy: While renewable energy costs have fallen significantly, they can still be higher than fossil fuels in some regions.
- Intermittency of Renewable Energy: Solar and wind energy are intermittent sources, meaning they are not always available when needed.
- Grid Integration Challenges: Integrating large amounts of renewable energy into existing grids can pose technical challenges.
- Infrastructure Investment: Building out new infrastructure for renewable energy and energy storage requires significant investments.
- Public Acceptance: Some communities may resist the construction of renewable energy projects, raising concerns about aesthetics or environmental impacts.
-
How will the energy transition impact jobs?
- The energy transition is expected to create new jobs in renewable energy, energy storage, and smart grid technologies. However, it may also lead to job losses in the fossil fuel sector.
- Governments and industry will need to implement strategies to support workers transitioning to new industries.
-
What role will artificial intelligence (AI) play in the energy transition?
- AI is expected to play a crucial role in optimizing energy systems, improving grid efficiency, and enabling predictive maintenance.
- AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and optimize energy flows, making the grid more reliable and efficient.
-
What are the implications of the energy transition for consumers?
- Consumers can expect to see lower energy costs, increased energy security, and greater control over their energy consumption.
- The transition to renewable energy will also lead to cleaner air and a healthier environment.
Tips for Navigating the Energy Transition:
- Invest in Energy Efficiency: Implement energy-efficient measures in your home or business to reduce energy consumption and lower your energy bills.
- Consider Renewable Energy: Explore options for generating your own renewable energy, such as rooftop solar panels or small-scale wind turbines.
- Support Energy Policy: Advocate for policies that promote renewable energy, energy efficiency, and a just transition to a clean energy economy.
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on the latest developments in the energy sector by following industry news and publications.
Conclusion:
The energy landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and a growing awareness of climate change. Trends in energy 2025 point towards a future that is cleaner, more efficient, and more resilient. The transition to a sustainable energy system presents both challenges and opportunities, requiring collaboration among governments, businesses, and consumers to navigate the path towards a cleaner and more sustainable future. By embracing these trends and actively participating in the energy transition, we can create a more prosperous and sustainable world for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Future of Energy: Trends Shaping the Landscape in 2025. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!