Navigating the Future of Water: Watershed Trends 2025
Related Articles: Navigating the Future of Water: Watershed Trends 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Future of Water: Watershed Trends 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Future of Water: Watershed Trends 2025
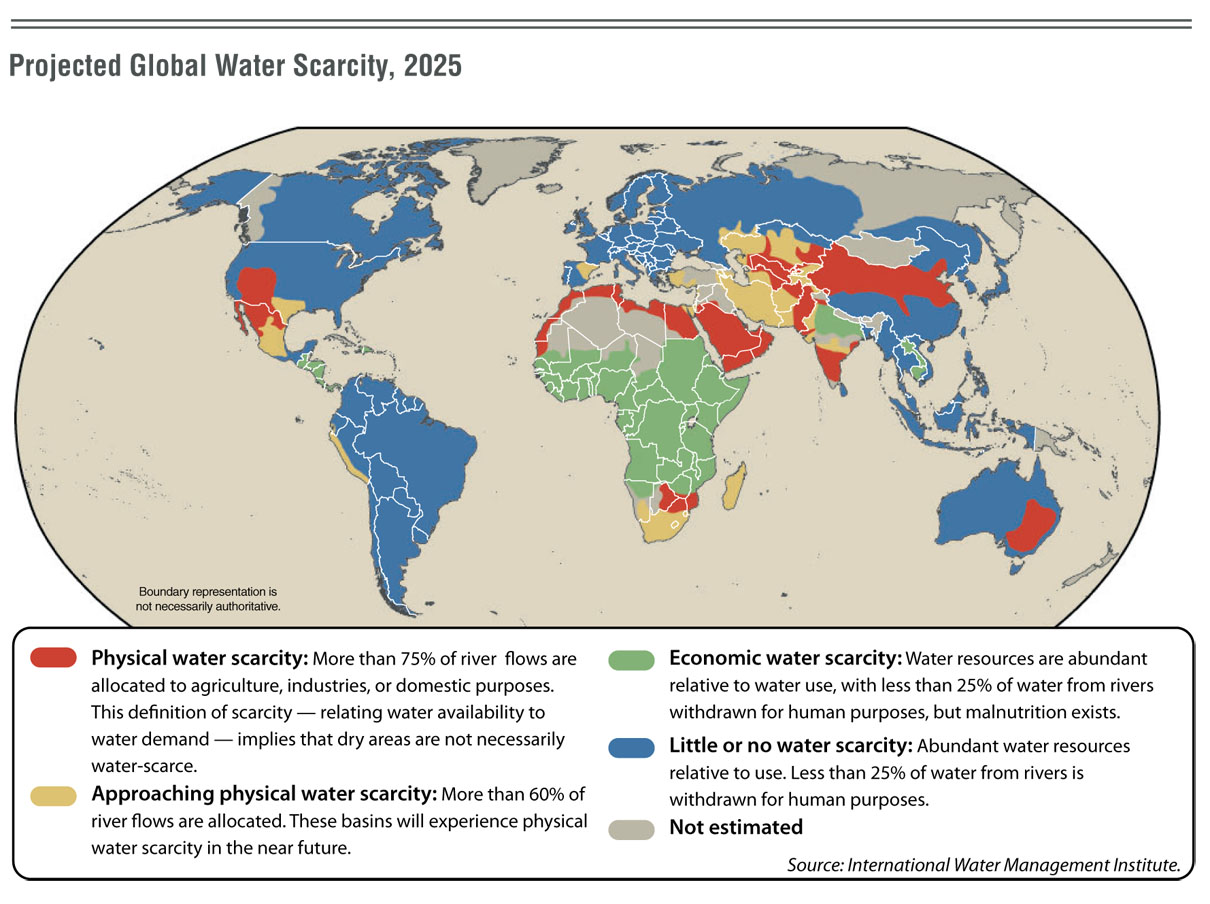
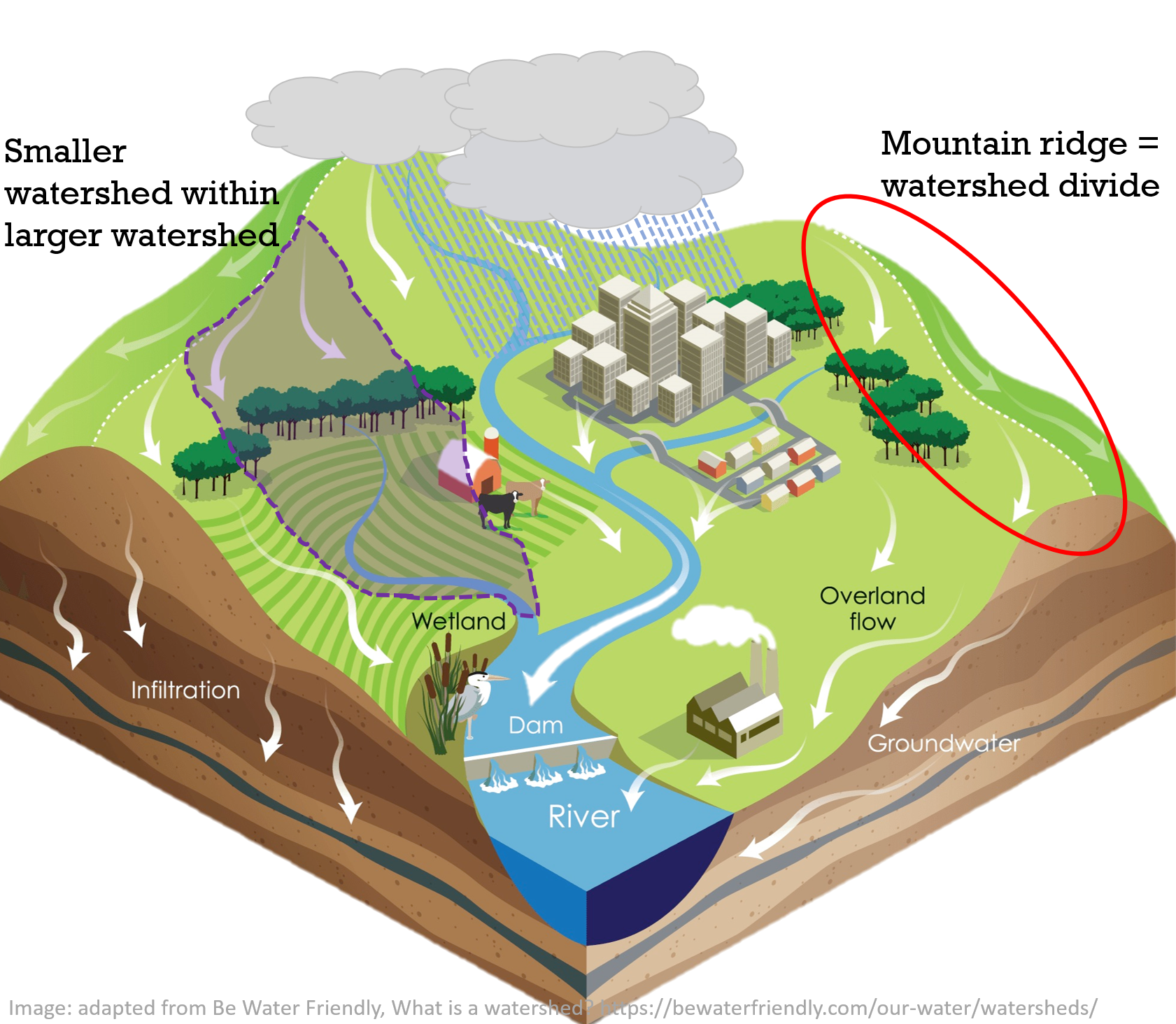
The world’s water resources are facing unprecedented challenges. Climate change, population growth, and increasing urbanization are putting immense strain on our watersheds, the areas of land where water collects and flows. Understanding the trends shaping these critical ecosystems is essential for ensuring a sustainable future. This exploration delves into the key watershed trends expected to define the year 2025, offering insights into their significance and implications.
1. Climate Change Impacts:
Climate change is altering precipitation patterns, leading to more frequent and intense droughts and floods. This disrupts the natural flow of water within watersheds, impacting water availability, water quality, and ecosystem health.
- Increased Variability in Precipitation: Warmer temperatures lead to increased evaporation, resulting in more intense rainfall events interspersed with longer dry periods. This variability makes water management challenging, requiring adaptation strategies to manage both floods and droughts.
- Glacier Melt and Snowpack Reduction: Rising temperatures are causing glaciers and snowpack to melt at accelerated rates, leading to reduced water availability downstream. This poses a significant threat to communities reliant on snowmelt for their water supply, particularly in mountainous regions.
- Sea Level Rise and Coastal Inundation: Rising sea levels threaten coastal watersheds, increasing the risk of saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources. This compromises water quality and can disrupt ecosystems, impacting fisheries and agriculture.
2. Population Growth and Urbanization:
As the global population continues to grow, particularly in urban areas, the demand for water resources is escalating. This puts pressure on watersheds to supply both drinking water and water for industrial and agricultural activities.
- Growing Water Demand: Increased population density in urban areas drives higher water consumption for domestic use, industry, and agriculture. This necessitates efficient water management strategies to meet growing demand without depleting water resources.
- Water Scarcity and Competition: Urbanization often leads to competition for water resources between different sectors. This can create conflict and necessitate collaborative approaches to ensure equitable access to water.
- Wastewater Management Challenges: Urban areas generate significant amounts of wastewater, which can pollute watersheds if not properly treated. Effective wastewater management systems are crucial for protecting water quality and promoting public health.
3. Land Use Change and Deforestation:
Changes in land use, including deforestation and urbanization, can have profound impacts on watersheds. Deforestation reduces the ability of land to absorb rainfall, leading to increased runoff and erosion, while urbanization creates impervious surfaces that impede water infiltration.
- Increased Runoff and Erosion: Deforestation and urbanization increase the rate of surface runoff, eroding soils and carrying pollutants into waterways. This can degrade water quality, harm aquatic ecosystems, and increase the risk of flooding.
- Reduced Water Infiltration: Impervious surfaces, such as roads and buildings, prevent rainwater from infiltrating the soil. This reduces groundwater recharge, diminishing water availability and increasing the risk of drought.
- Loss of Ecosystem Services: Forests and wetlands provide valuable ecosystem services, such as water filtration and flood control. Their destruction undermines these services, impacting the health of watersheds and surrounding communities.
4. Water Pollution and Contamination:
Pollution from various sources, including agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and sewage overflows, can contaminate watersheds, jeopardizing water quality and public health.
- Agricultural Runoff: Fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste from agricultural activities can contaminate waterways, leading to eutrophication, algal blooms, and harmful bacteria growth.
- Industrial Discharges: Industrial facilities often release wastewater containing toxic chemicals and heavy metals, posing serious risks to human and ecological health.
- Sewage Overflows: Aging sewage infrastructure can lead to overflows, releasing untreated wastewater into waterways, contaminating water sources and spreading diseases.
5. Emerging Technologies and Innovations:
Technological advancements are playing an increasingly crucial role in water management and watershed protection. Innovations in data collection, monitoring, and treatment technologies are offering new solutions to address water challenges.
- Remote Sensing and Data Analytics: Satellites and drones equipped with sensors can provide real-time data on water quality, precipitation, and land cover changes, enabling better monitoring and prediction of watershed conditions.
- Smart Water Management Systems: Advanced technologies, such as smart meters and automated irrigation systems, can optimize water use, reduce waste, and improve efficiency in urban and agricultural settings.
- Water Treatment Innovations: New technologies are emerging for treating wastewater, desalination, and removing contaminants from water sources, enhancing water quality and expanding access to safe drinking water.
6. Water Governance and Policy:
Effective water governance and policies are essential for managing watersheds sustainably. This includes developing water allocation strategies, promoting collaborative water management, and enforcing environmental regulations.
- Integrated Water Resource Management: A holistic approach to water management that considers the interconnectedness of water resources within watersheds, aiming to balance competing demands and ensure sustainable use.
- Water Rights and Allocation: Clear and equitable water rights allocation systems are essential for preventing conflicts and ensuring fair access to water resources.
- Environmental Regulations and Enforcement: Strong environmental regulations and effective enforcement mechanisms are crucial for protecting water quality, preventing pollution, and mitigating the impacts of human activities on watersheds.
7. Public Engagement and Education:
Raising public awareness about the importance of watersheds and promoting responsible water use are crucial for fostering sustainable water management practices.
- Citizen Science Initiatives: Engaging citizens in water monitoring and data collection can contribute to a better understanding of watershed health and empower communities to take action.
- Education and Outreach Programs: Educating the public about watershed issues, water conservation techniques, and the importance of responsible water use is essential for promoting sustainable practices.
- Community-Based Water Management: Involving communities in decision-making processes related to water management can foster local ownership and ensure that water resources are managed in a way that meets local needs and priorities.
8. International Cooperation and Collaboration:
Watersheds often extend beyond national borders, requiring international cooperation to address transboundary water issues and ensure sustainable management of shared resources.
- Transboundary Water Agreements: Formal agreements between countries sharing watersheds are essential for establishing water allocation mechanisms, resolving disputes, and promoting collaborative management of shared resources.
- Information Sharing and Capacity Building: Sharing data, expertise, and best practices across borders can enhance understanding of watershed dynamics and promote the development of effective water management strategies.
- Global Water Governance: International organizations play a crucial role in promoting global water security, coordinating international efforts, and providing technical assistance to countries facing water challenges.
Related Searches:
- Watershed Management Strategies: Explore different approaches to managing watersheds, including best practices for water conservation, pollution control, and ecosystem restoration.
- Watershed Health Assessment: Learn about methods for assessing the health of watersheds, including water quality monitoring, habitat assessment, and ecological indicators.
- Watershed Restoration and Rehabilitation: Discover techniques for restoring degraded watersheds, including reforestation, wetland restoration, and streambank stabilization.
- Watershed Modeling: Understand how computer models are used to simulate water flow, predict water availability, and evaluate the impacts of different management scenarios.
- Watershed Education and Outreach: Explore resources and strategies for educating the public about watersheds and promoting responsible water use.
- Watershed-Based Management Plans: Learn about the development and implementation of comprehensive watershed management plans that address specific local needs and challenges.
- Watershed Governance and Policy: Explore the role of government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and communities in watershed management and the development of effective water policies.
- Watershed Sustainability: Understand the principles of sustainable watershed management and the importance of balancing human needs with the ecological integrity of these vital ecosystems.
FAQs by Watershed Trends 2025:
Q: How will climate change impact watersheds in the future?
A: Climate change will exacerbate existing water challenges by altering precipitation patterns, leading to more frequent and intense droughts and floods. This will disrupt the natural flow of water within watersheds, impacting water availability, water quality, and ecosystem health.
Q: What are the implications of population growth and urbanization on watersheds?
A: Increased population density will lead to greater water demand for domestic use, industry, and agriculture. This will put pressure on watersheds to supply sufficient water while managing wastewater effectively to prevent pollution.
Q: How can technology help address watershed challenges?
A: Emerging technologies like remote sensing, smart water management systems, and advanced water treatment methods offer innovative solutions for monitoring, managing, and protecting watersheds.
Q: What role does public engagement play in watershed management?
A: Public awareness, education, and citizen participation are crucial for promoting responsible water use, supporting watershed restoration efforts, and ensuring that water resources are managed sustainably.
Q: What are the key challenges to effective watershed management?
A: Challenges include balancing competing water demands, managing pollution from multiple sources, addressing the impacts of land use change, and ensuring equitable access to water resources.
Q: How can we ensure a sustainable future for our watersheds?
A: Sustainable watershed management requires a holistic approach that considers the interconnectedness of water resources, promotes collaborative decision-making, and integrates technological advancements with responsible water use practices.
Tips by Watershed Trends 2025:
- Conserve Water: Adopt water-saving practices in your home, garden, and workplace.
- Reduce Pollution: Minimize your use of fertilizers and pesticides, dispose of chemicals responsibly, and support efforts to reduce industrial discharges.
- Support Watershed Restoration: Get involved in local initiatives to restore degraded watersheds, such as planting trees, cleaning up waterways, or advocating for environmental protection.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Learn about watershed issues and share your knowledge with others to promote awareness and responsible water use.
- Advocate for Policy Change: Support policies that promote sustainable water management, protect water quality, and address the impacts of climate change.
Conclusion by Watershed Trends 2025:
The future of our watersheds is intricately linked to our ability to adapt to changing conditions and manage these vital ecosystems sustainably. By understanding the key trends shaping watersheds in 2025, we can develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks, enhance water security, and ensure the long-term health of these essential resources. Collaborative efforts, informed by scientific understanding and driven by public engagement, are crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in the management of our watersheds.



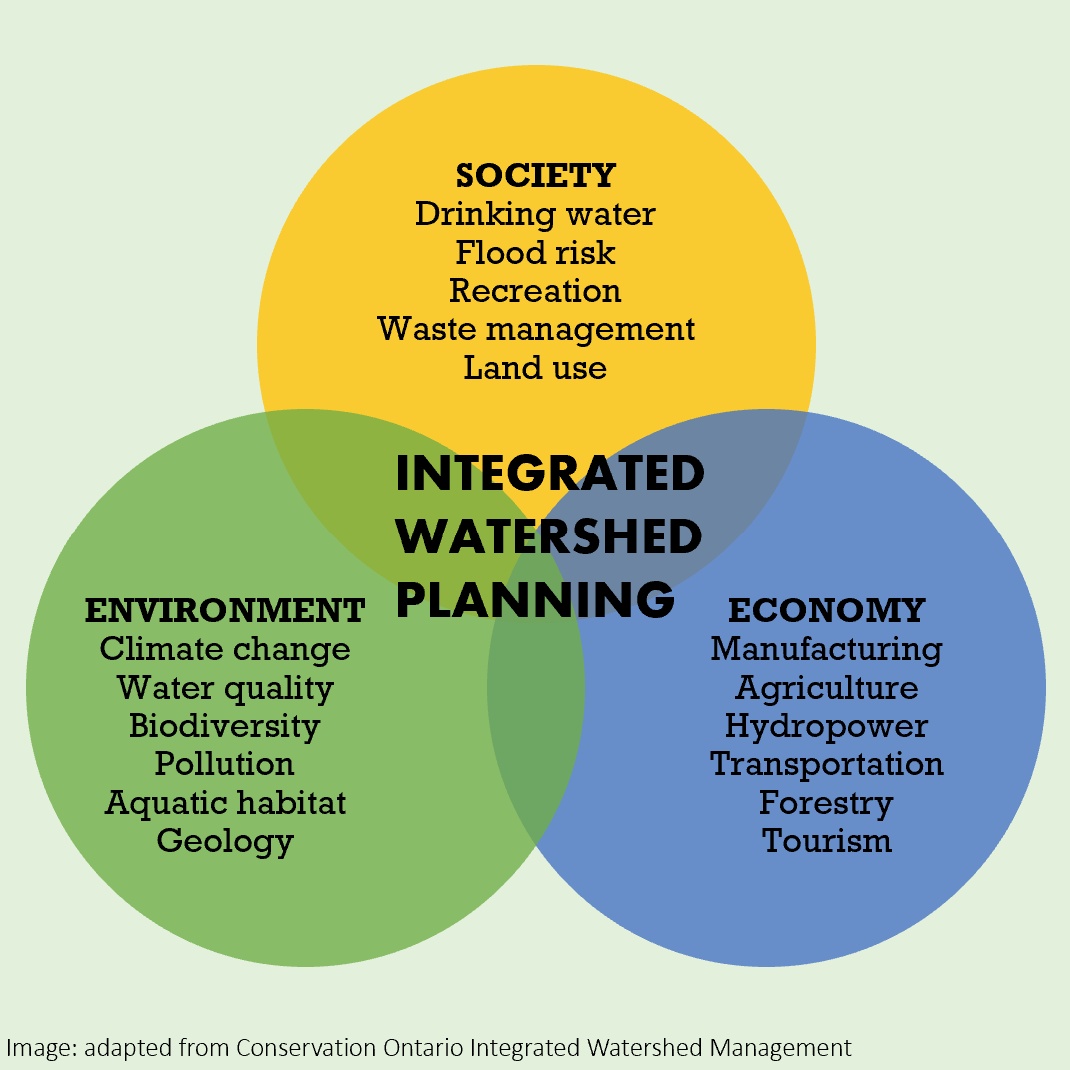
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Future of Water: Watershed Trends 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!