The Periodic Table: A Roadmap to Understanding the Elements and Shaping the Future
Related Articles: The Periodic Table: A Roadmap to Understanding the Elements and Shaping the Future
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Periodic Table: A Roadmap to Understanding the Elements and Shaping the Future. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Periodic Table: A Roadmap to Understanding the Elements and Shaping the Future
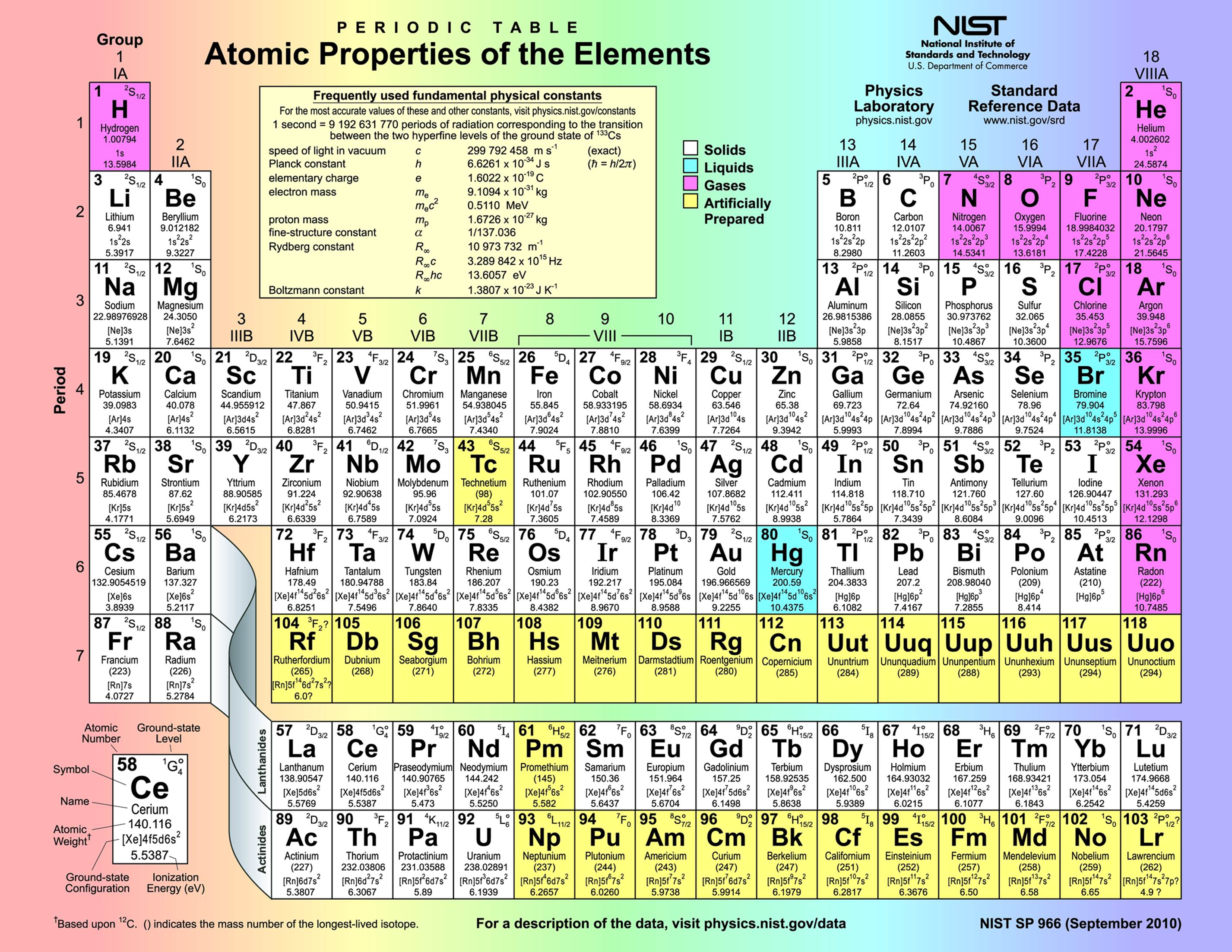
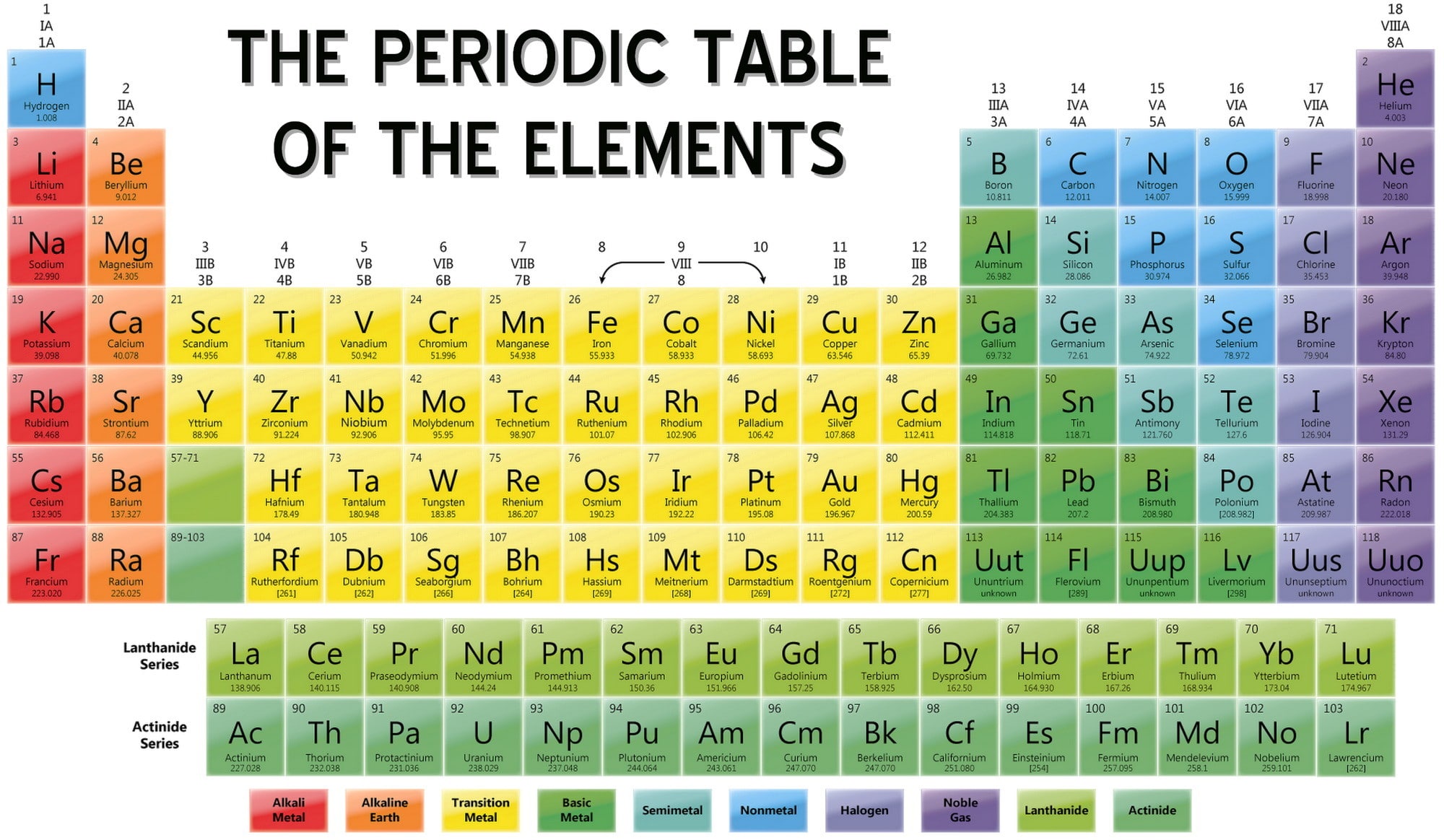
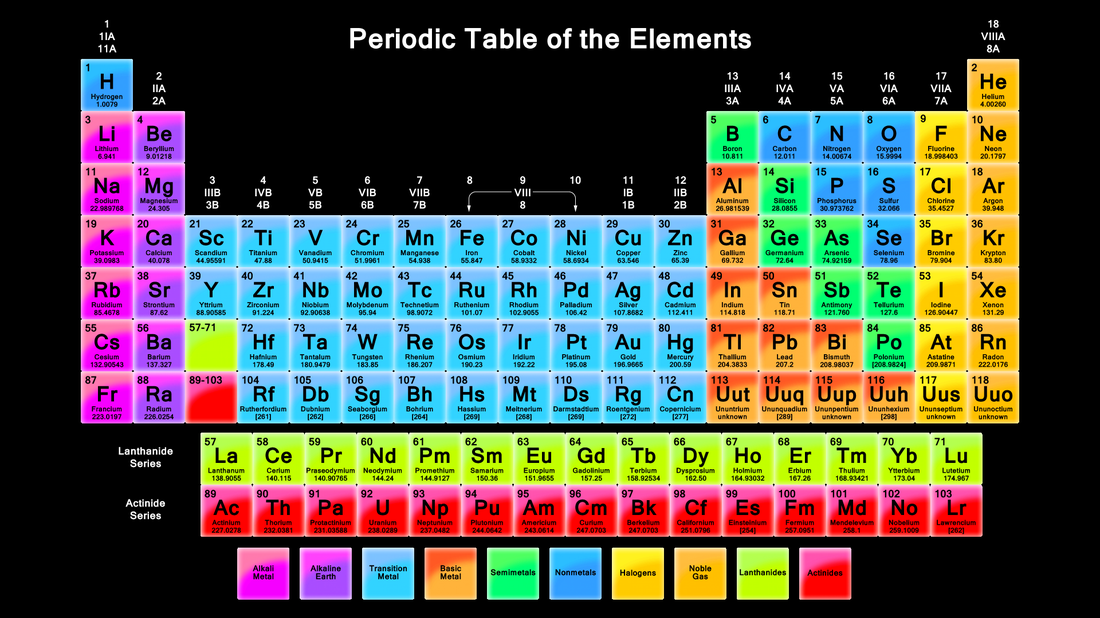
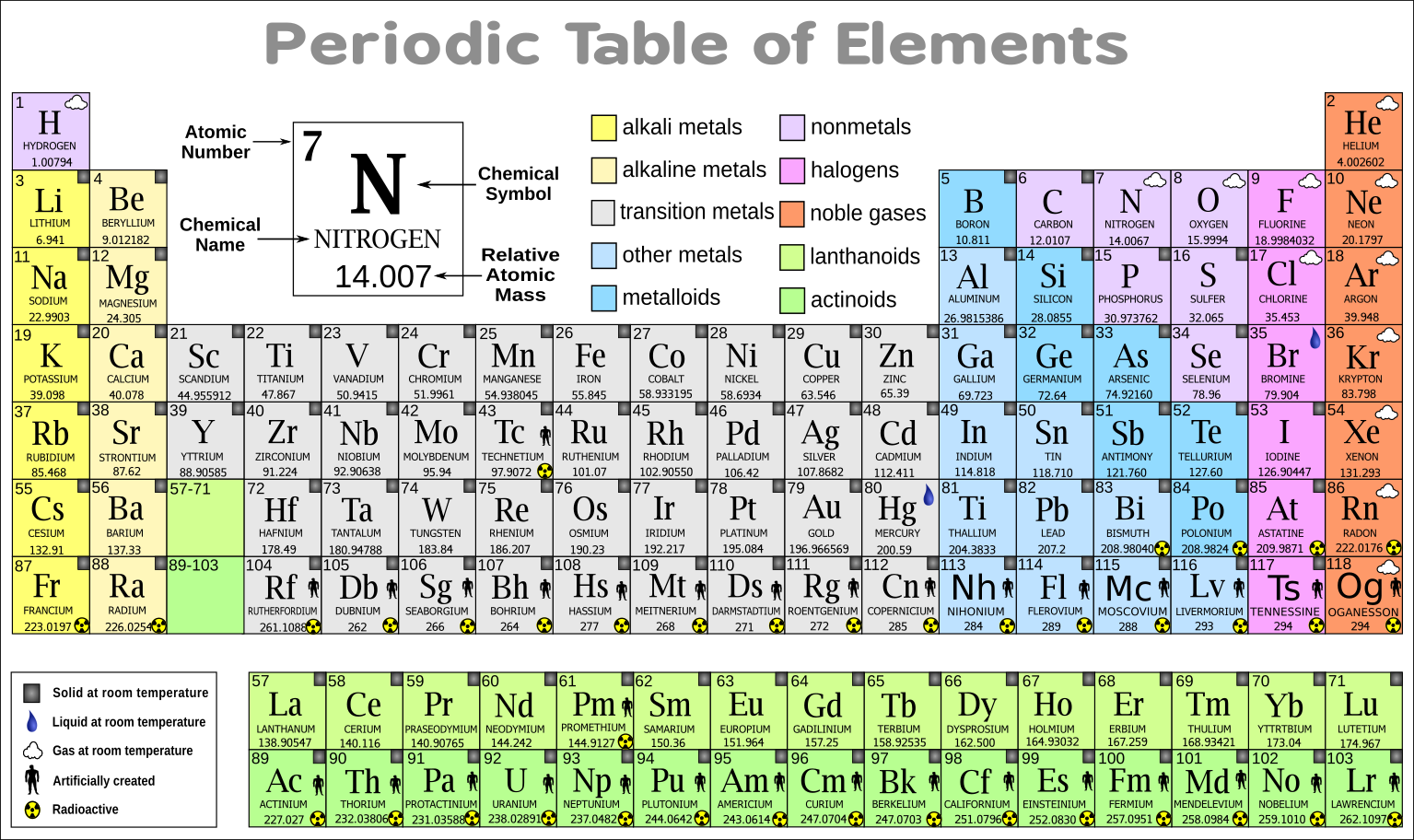
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, is more than just a chart of elements. It’s a powerful tool that reveals the fundamental building blocks of our universe and allows us to predict their behavior. Understanding the periodic table is crucial for advancements in various fields, including medicine, materials science, and energy production.
Periodic Table and Trends 2025
As we look toward 2025, the periodic table remains an indispensable guide for scientific exploration and technological innovation. The trends emerging in this field are shaping the future of materials, energy, and medicine, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries and solutions to global challenges.
Understanding the Periodic Table: A Foundation for Exploration
The periodic table is organized by atomic number, which represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. Elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together in columns known as groups, and rows known as periods. This arrangement reflects the underlying structure of atoms and their tendency to form bonds with other elements.
Key Trends in the Periodic Table: Shaping the Future of Science and Technology
1. The Rise of Advanced Materials:
The periodic table serves as a blueprint for designing materials with specific properties. Scientists are actively exploring new combinations of elements to create materials with enhanced strength, conductivity, and resilience. For instance, the development of graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice, has revolutionized electronics and materials science.
- Nanomaterials: The manipulation of materials at the nanoscale, often involving elements like silicon, gold, and silver, is leading to the development of novel catalysts, sensors, and drug delivery systems.
- High-Entropy Alloys: These alloys, containing multiple elements in near-equal proportions, exhibit remarkable properties such as high strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.
2. The Quest for Clean Energy:
The periodic table holds the key to unlocking sustainable energy sources. Elements like lithium, cobalt, and nickel are crucial components in batteries, while silicon and solar cells are essential for harnessing solar energy.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Research is focused on developing more efficient and affordable batteries using elements like lithium-ion, sodium-ion, and magnesium-ion chemistries.
- Nuclear Fusion: The potential of nuclear fusion as a clean energy source relies on the understanding of elements like deuterium and tritium, which are isotopes of hydrogen.
3. The Advancements in Medicine and Biotechnology:
The periodic table plays a vital role in developing new drugs, diagnostic tools, and medical therapies. Elements like platinum are used in cancer treatments, while iodine is essential for thyroid function.
- Targeted Drug Delivery: Utilizing elements like gold nanoparticles, scientists are developing targeted drug delivery systems that can deliver medications directly to specific cells, minimizing side effects.
- Medical Imaging: Elements like technetium and iodine are used in various medical imaging techniques, enabling doctors to diagnose and monitor diseases effectively.
4. The Exploration of New Elements:
The periodic table is constantly evolving as scientists discover new elements. The synthesis of superheavy elements, like tennessine and oganesson, pushes the boundaries of our understanding of atomic structure and nuclear physics.
- Superheavy Elements: The discovery of new elements offers insights into the stability and properties of atomic nuclei, shedding light on the fundamental forces that govern the universe.
- Theoretical Predictions: Theoretical models based on the periodic table are used to predict the existence and properties of yet-to-be discovered elements, guiding future research.
Related Searches and FAQs:
1. Periodic Table Trends:
-
What are the major trends in the periodic table?
- The major trends in the periodic table include electronegativity, ionization energy, atomic radius, and electron affinity. These trends are crucial for understanding the chemical behavior of elements and predicting their reactivity.
-
How do these trends affect chemical reactions?
- The trends in the periodic table influence the formation of bonds between atoms, determining the type and strength of chemical reactions. For example, elements with high electronegativity tend to attract electrons, leading to the formation of ionic bonds.
-
Are there any exceptions to these trends?
- Yes, there are exceptions to the trends in the periodic table due to the complex interplay of factors like electron configuration and shielding effects. Understanding these exceptions is essential for a deeper understanding of atomic behavior.
2. Periodic Table Groups and Periods:
-
What are the different groups in the periodic table?
- The periodic table is divided into 18 groups, each representing a column of elements with similar chemical properties. For example, Group 1 contains alkali metals, Group 2 contains alkaline earth metals, and Group 17 contains halogens.
-
What are the different periods in the periodic table?
- The periodic table has seven periods, each representing a row of elements with the same number of electron shells. Elements in the same period have similar electron configurations, leading to similar chemical properties.
-
How do group and period numbers relate to atomic structure?
- Group number indicates the number of valence electrons, while period number indicates the number of electron shells. This information is crucial for understanding the chemical behavior and bonding properties of elements.
3. Periodic Table Applications:
-
How is the periodic table used in chemistry?
- The periodic table is fundamental to chemistry, providing a framework for understanding the properties and reactions of elements. It allows chemists to predict the behavior of elements in different environments and design new materials with specific properties.
-
How is the periodic table used in materials science?
- Materials scientists use the periodic table to design new materials with tailored properties, such as strength, conductivity, and resilience. By understanding the properties of different elements, they can create materials suitable for specific applications.
-
How is the periodic table used in medicine?
- The periodic table is essential in medicine, as elements like platinum, iodine, and technetium play crucial roles in various medical treatments and diagnostic tools. Understanding the properties of these elements is crucial for developing effective therapies and imaging techniques.
4. Periodic Table History:
-
Who discovered the periodic table?
- The credit for the discovery of the periodic table is generally given to Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, who published his version of the periodic table in 1869. However, other scientists, like Lothar Meyer, also contributed to the development of the periodic table.
-
How has the periodic table evolved over time?
- The periodic table has evolved significantly since its initial discovery, with new elements being discovered and the understanding of atomic structure becoming more sophisticated. The modern periodic table reflects our current understanding of the fundamental nature of matter.
-
What are some of the key milestones in the history of the periodic table?
- Key milestones include the discovery of new elements, the development of quantum mechanics, and the understanding of isotopes. These milestones have led to a more comprehensive and accurate understanding of the periodic table.
5. Periodic Table Trends and Technology:
-
How do trends in the periodic table influence technological advancements?
- Trends in the periodic table, such as electronegativity and ionization energy, influence the development of new materials, energy sources, and medical therapies. By understanding these trends, scientists can create technologies with enhanced efficiency, sustainability, and effectiveness.
-
What are some examples of how the periodic table has shaped technology?
- The periodic table has played a crucial role in the development of transistors, solar cells, batteries, and medical imaging techniques. These technologies have transformed various aspects of our lives, from communication and energy production to healthcare and diagnostics.
-
What are some future applications of the periodic table in technology?
- The periodic table will continue to be a driving force in technological advancements. Future applications include the development of new materials with exceptional properties, efficient energy storage solutions, and personalized medicine tailored to individual genetic profiles.
6. Periodic Table and the Future:
-
What are some of the challenges facing the periodic table in the future?
- Challenges include the need for sustainable sourcing of critical elements, the development of new technologies for element separation and purification, and the ethical considerations surrounding the use of certain elements.
-
How can the periodic table help us address global challenges?
- The periodic table can play a crucial role in addressing global challenges like climate change, resource depletion, and disease outbreaks. By understanding the properties of different elements, we can develop innovative solutions for sustainable energy, clean water, and effective healthcare.
-
What are some of the exciting opportunities for the periodic table in the future?
- Exciting opportunities include the discovery of new elements, the development of advanced materials with unprecedented properties, and the creation of new technologies that can address global challenges and improve human well-being.
Tips for Using the Periodic Table:
- Focus on Trends: Understanding the major trends in the periodic table, such as electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic radius, is crucial for predicting the chemical behavior of elements.
- Group and Period Relationships: Recognize the relationships between groups and periods in the periodic table. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to their similar electron configurations, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
- Electron Configuration: Understand the electron configuration of elements and how it relates to their chemical behavior. The arrangement of electrons in an atom’s shells determines its reactivity and bonding properties.
- Periodic Table Resources: Utilize online resources and textbooks that provide detailed information about the periodic table, its trends, and applications. These resources can help you deepen your understanding of this fundamental tool.
Conclusion:
The periodic table is a powerful tool that provides a framework for understanding the fundamental building blocks of our universe. By understanding the trends and relationships within the periodic table, we can predict the behavior of elements, design new materials, develop innovative technologies, and address global challenges. As we look towards 2025, the periodic table will continue to be a guiding force in scientific exploration and technological innovation, shaping the future of our world.
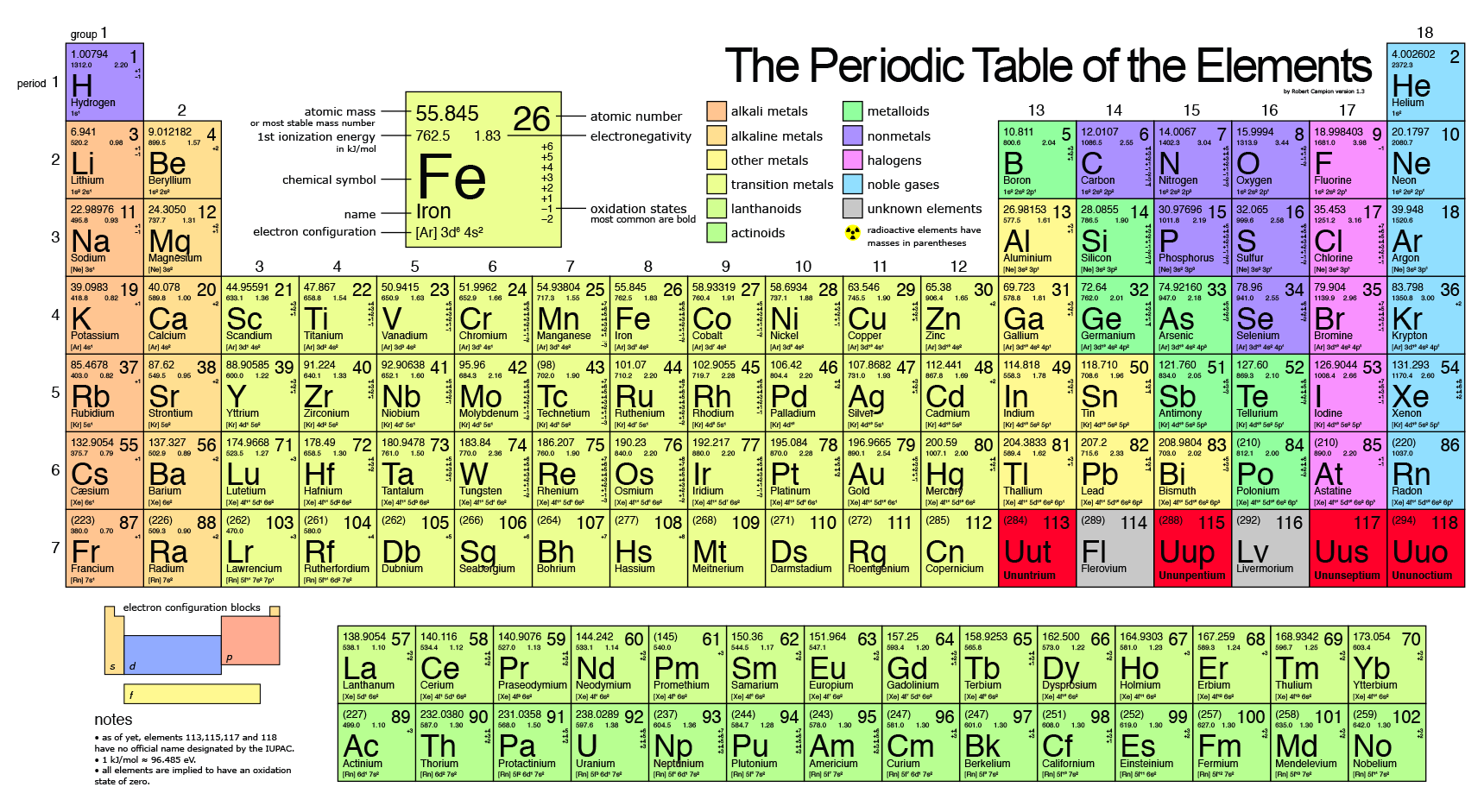
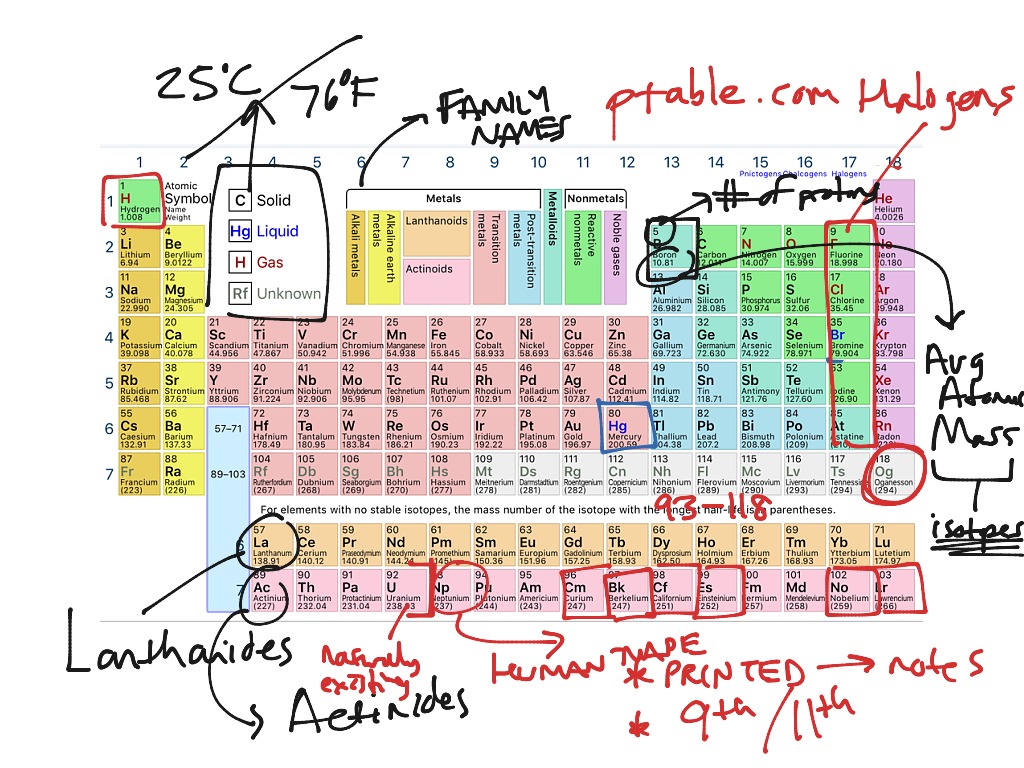
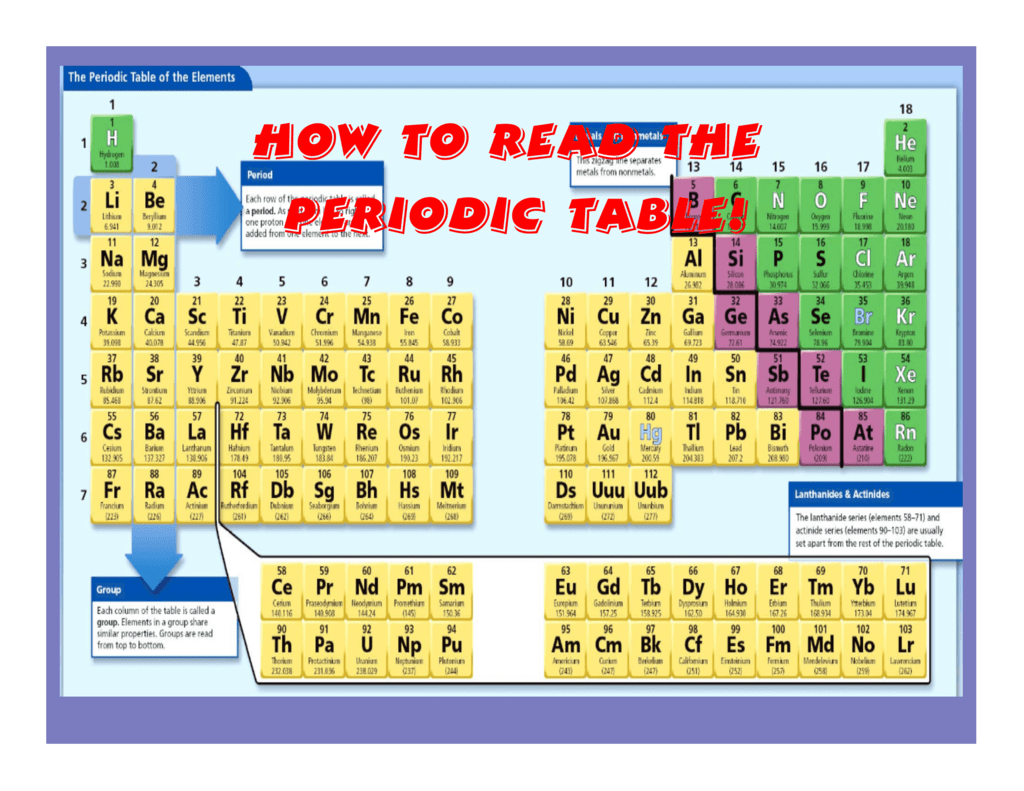


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Periodic Table: A Roadmap to Understanding the Elements and Shaping the Future. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!