Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, arranges elements in a systematic way, revealing fascinating patterns in their properties. These patterns, known as periodic trends, are crucial for understanding the behavior of elements and predicting their reactivity. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of periodic trends, their implications, and their application in various fields.
Periodic Trends: Unveiling the Patterns
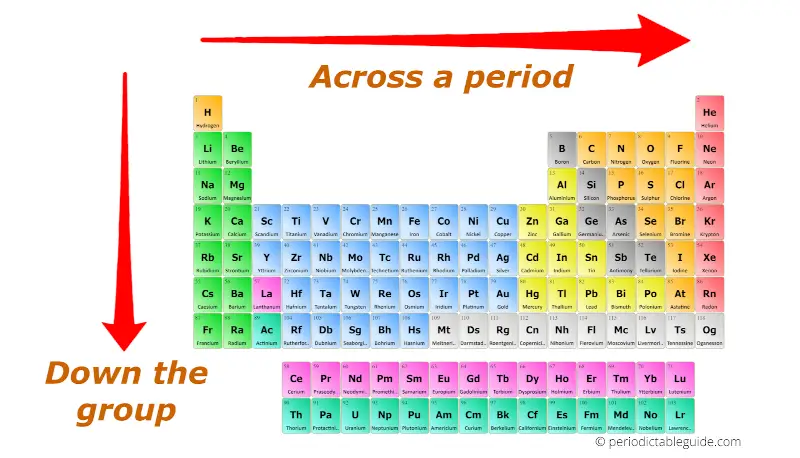
Periodic trends refer to the systematic variations in the properties of elements as one moves across a period (horizontal row) or down a group (vertical column) of the periodic table. These trends are primarily governed by:
-
Atomic Radius: The distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell of an atom. Atomic radius generally decreases across a period due to increasing nuclear charge, which attracts electrons more strongly, pulling them closer to the nucleus. Conversely, atomic radius increases down a group as the number of electron shells increases, leading to a larger atomic size.
-
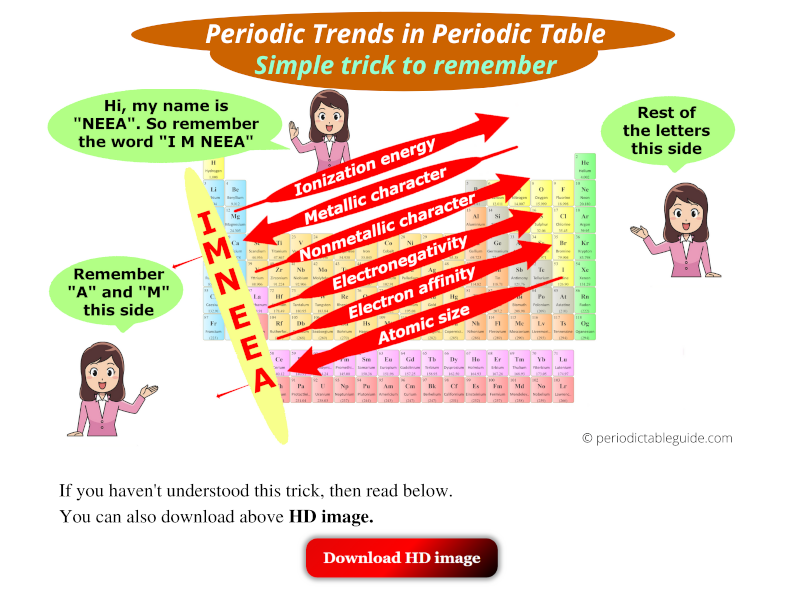
Ionization Energy: The minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom in its ground electronic state. Ionization energy generally increases across a period due to the increasing nuclear charge, making it harder to remove an electron. Conversely, ionization energy decreases down a group as the outermost electron is further from the nucleus, requiring less energy to remove it.
-
Electron Affinity: The change in energy when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form a negative ion. Electron affinity generally increases across a period due to the increasing nuclear charge, which attracts the added electron more strongly. Down a group, electron affinity generally decreases as the added electron enters a higher energy level, experiencing weaker attraction to the nucleus.
-
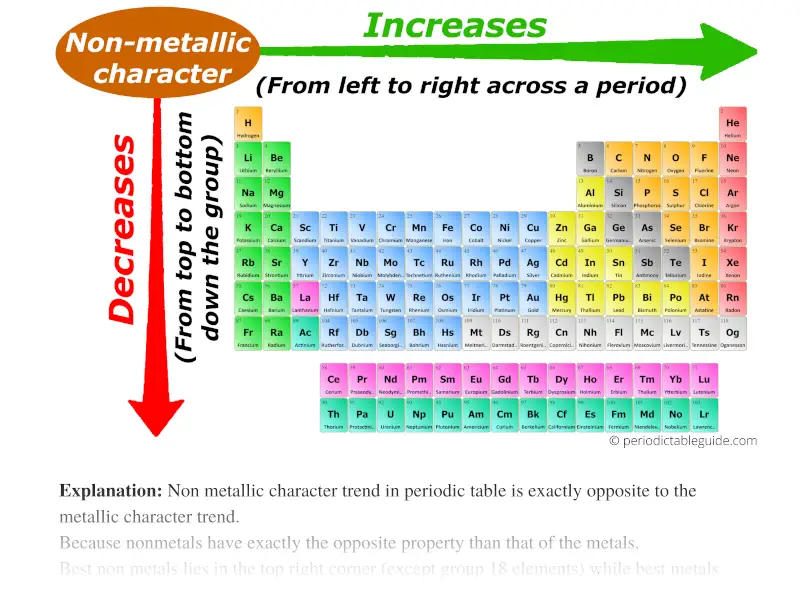
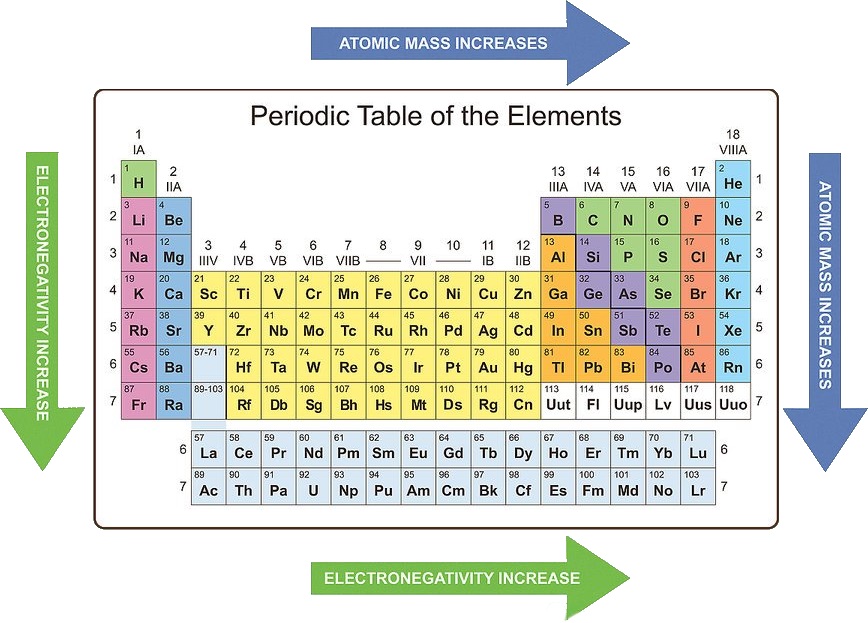
Electronegativity: The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons towards itself. Electronegativity generally increases across a period due to the increasing nuclear charge, making the atom more attractive to electrons. It decreases down a group as the outermost electron is further from the nucleus, experiencing weaker attraction.
Applications of Periodic Trends
Understanding periodic trends is paramount in various fields, including:
-
Predicting Chemical Reactions: Periodic trends allow us to predict the reactivity of elements and the type of chemical bonds they form. For instance, elements with high electronegativity tend to form ionic bonds with elements having low electronegativity.
-
Designing New Materials: Knowledge of periodic trends is essential in materials science, where researchers leverage the properties of elements to design novel materials with specific characteristics. For example, understanding the trend in melting point helps in selecting suitable materials for high-temperature applications.
-
Understanding Biological Processes: Periodic trends play a role in understanding the function of biological molecules. For instance, the variation in electronegativity among elements in biological molecules contributes to their specific interactions and functions.
-
Environmental Chemistry: Periodic trends are crucial for understanding the behavior of elements in the environment. For example, understanding the trend in reactivity helps in assessing the environmental impact of pollutants and developing strategies for remediation.
The Importance of WebQuests
WebQuests are interactive learning activities that guide students through a series of online resources to explore a specific topic. In the context of periodic trends, webquests can be valuable tools for:
-
Engaging Students: WebQuests provide a dynamic and interactive learning experience, making the study of periodic trends more engaging and stimulating.
-
Developing Critical Thinking Skills: WebQuests encourage students to analyze information from various sources, evaluate its credibility, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
-
Enhancing Research Skills: WebQuests expose students to a variety of online resources, teaching them how to effectively navigate and utilize these resources for research purposes.
-
Promoting Collaboration: Some webquests encourage group work, fostering collaboration and communication skills among students.
FAQs on Periodic Trends and WebQuests
Q: What are the major periodic trends?
A: The major periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity.
Q: How do periodic trends affect chemical reactivity?
A: Periodic trends influence the reactivity of elements by determining their ability to gain or lose electrons, forming chemical bonds.
Q: What are the benefits of using webquests in learning about periodic trends?
A: Webquests offer engaging, interactive, and collaborative learning experiences, enhancing critical thinking, research skills, and information literacy.
Q: What are some examples of webquests related to periodic trends?
A: Numerous webquests on periodic trends are available online, focusing on specific aspects like the trends in atomic radius, ionization energy, or the application of periodic trends in predicting chemical reactions.
Tips for Effective WebQuest Design and Implementation
-
Clear Learning Objectives: Define specific and measurable learning objectives for the webquest.
-
Engaging Introduction: Start with an intriguing scenario or question to capture students’ attention.
-
Well-Structured Tasks: Break down the webquest into manageable tasks with clear instructions.
-
Variety of Resources: Include a mix of text, images, videos, and interactive simulations.
-
Assessment: Incorporate assessment activities to evaluate students’ understanding.
-
Reflection: Encourage students to reflect on their learning process and the insights gained.
Conclusion
Understanding periodic trends is fundamental to comprehending the behavior of elements and their interactions. Webquests offer a dynamic and engaging approach to learning about these trends, fostering critical thinking, research skills, and collaboration. By leveraging the power of webquests, educators can make the study of periodic trends a more interactive and meaningful experience for students.
.PNG)
/periodictrendstable-5c4a46614cedfd000187c5db.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!