Understanding the Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide to Chemical Properties
Related Articles: Understanding the Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide to Chemical Properties
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide to Chemical Properties. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide to Chemical Properties
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide to Chemical Properties
- 3.1 Key Periodic Trends
- 3.2 Chemistry periodic trends worksheet answers 2025 and Their Importance
- 3.3 Related Searches
- 3.4 FAQs
- 3.5 Tips for Mastering Periodic Trends
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide to Chemical Properties
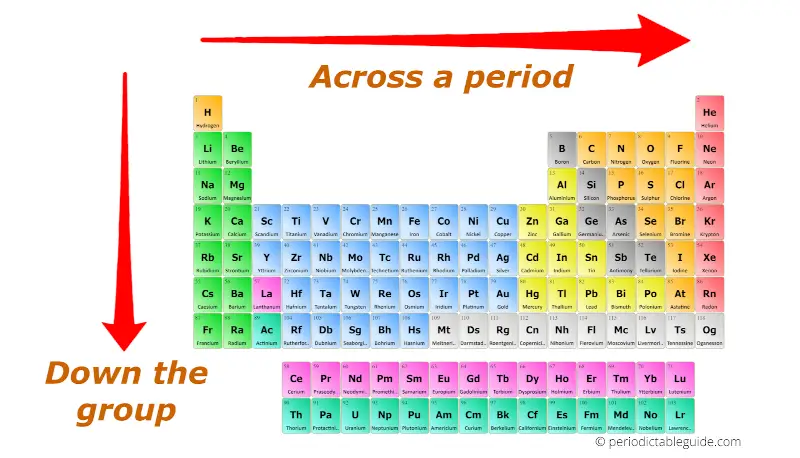
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, organizing elements based on their atomic structure and resulting properties. Chemistry periodic trends worksheet answers 2025 refer to the predictable patterns observed in these properties as one moves across a period (horizontal row) or down a group (vertical column) of the periodic table. Mastering these trends enables chemists to predict and explain the behavior of elements and their compounds, facilitating a deeper understanding of chemical reactions and the world around us.
Key Periodic Trends
Several essential periodic trends govern the behavior of elements:
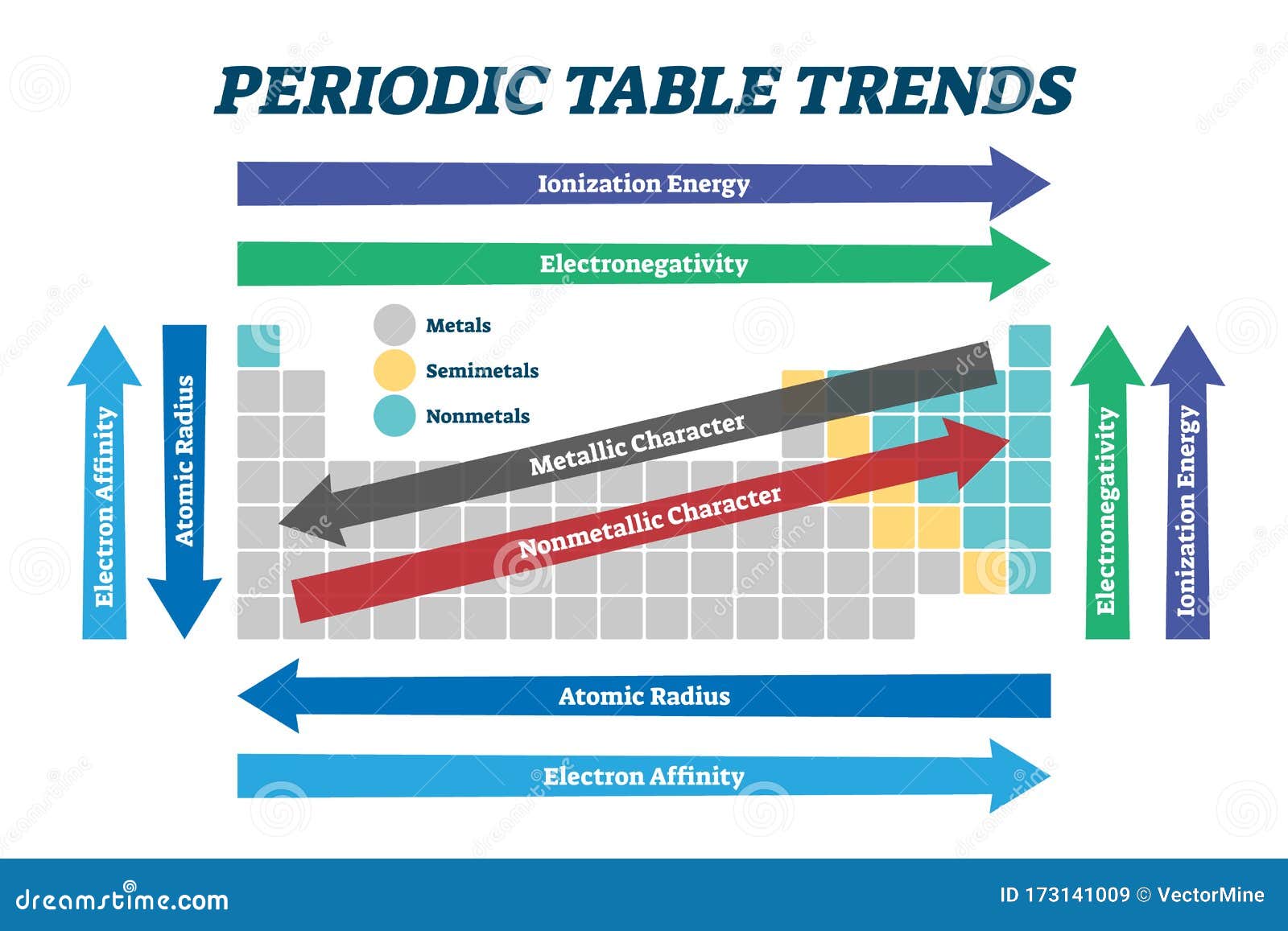
1. Atomic Radius: The atomic radius refers to the distance between the nucleus of an atom and its outermost electron shell.
- Trend: Atomic radius generally increases as you move down a group and decreases as you move across a period.
- Explanation: Moving down a group, electrons occupy higher energy levels, which are further from the nucleus. Across a period, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, attracting the electrons more strongly and pulling them closer to the nucleus, resulting in a smaller atomic radius.
2. Ionization Energy: Ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom in its ground state.
- Trend: Ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Explanation: Across a period, the increasing nuclear charge holds electrons more tightly, making it harder to remove them. Down a group, the outermost electron is further from the nucleus and shielded by inner electrons, making it easier to remove.
3. Electron Affinity: Electron affinity measures the change in energy when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to form a negative ion.
- Trend: Electron affinity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group. However, there are exceptions, particularly for elements with half-filled or fully-filled electron shells.
- Explanation: Across a period, the increasing nuclear charge attracts incoming electrons more strongly, leading to a more negative electron affinity. Down a group, the outermost electron is further from the nucleus and shielded by inner electrons, reducing the attraction for an additional electron.
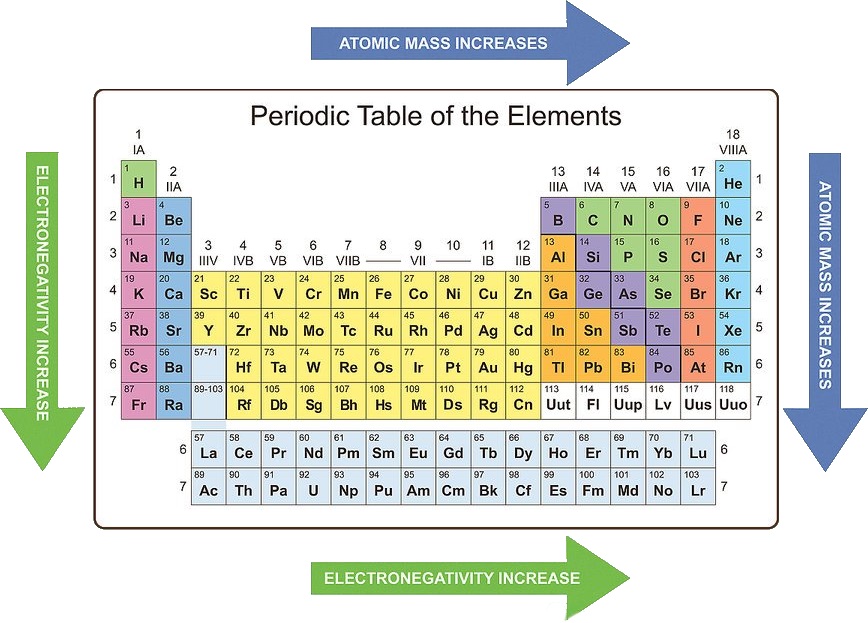
4. Electronegativity: Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond.
- Trend: Electronegativity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
- Explanation: Across a period, the increasing nuclear charge attracts electrons more strongly, leading to higher electronegativity. Down a group, the increasing distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron reduces the attraction for shared electrons.
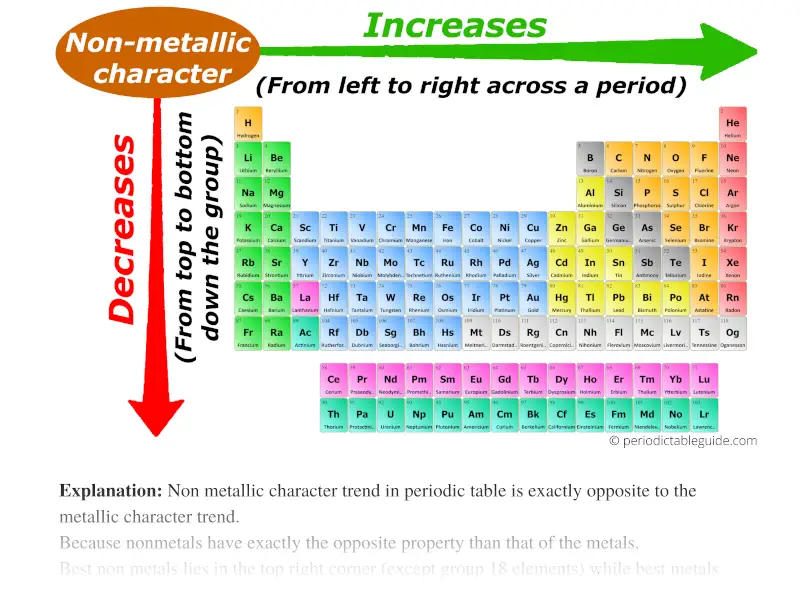
5. Metallic Character: Metallic character refers to the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions (cations).
- Trend: Metallic character generally increases down a group and decreases across a period.
- Explanation: Down a group, the outermost electron is further from the nucleus and more easily lost, leading to increased metallic character. Across a period, the increasing nuclear charge holds electrons more tightly, making it less likely to lose them.
Chemistry periodic trends worksheet answers 2025 and Their Importance
Chemistry periodic trends worksheet answers 2025 are essential for understanding and predicting the behavior of elements and compounds. They provide a framework for:
- Predicting Chemical Reactions: By understanding the trends in electronegativity, ionization energy, and electron affinity, chemists can predict the type of bonds that will form between atoms and the likelihood of a reaction occurring.
- Understanding Chemical Properties: The trends in atomic radius, ionization energy, and electron affinity explain the differences in reactivity, boiling point, and melting point observed among elements.
- Designing New Materials: By knowing the periodic trends, scientists can design new materials with specific properties, such as high conductivity or strength, by strategically combining elements with desired characteristics.
Related Searches
Chemistry periodic trends worksheet answers 2025 is a broad term encompassing various aspects of chemical properties. Here are some related searches that delve deeper into specific areas:
1. Periodic Trends in Reactivity: This search explores how periodic trends influence the reactivity of elements, explaining why alkali metals are highly reactive, while noble gases are inert.
2. Periodic Trends in Bonding: This search focuses on how periodic trends affect the types of bonds formed between atoms, including ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds.
3. Periodic Trends in Physical Properties: This search delves into how periodic trends relate to physical properties like melting point, boiling point, and density.
4. Periodic Trends in Chemical Reactions: This search examines how periodic trends influence the types of chemical reactions that elements participate in, such as oxidation-reduction reactions.
5. Periodic Trends in Nuclear Chemistry: This search explores how periodic trends relate to nuclear properties like radioactive decay and nuclear stability.
6. Periodic Trends in Organic Chemistry: This search focuses on how periodic trends impact the structure and reactivity of organic molecules, including functional groups and reaction mechanisms.
7. Periodic Trends in Biochemistry: This search examines how periodic trends influence the behavior of biomolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates.
8. Periodic Trends in Environmental Chemistry: This search investigates how periodic trends affect the fate and transport of pollutants in the environment, including heavy metals and radioactive elements.
FAQs
1. What are the main factors that influence periodic trends?
The main factors influencing periodic trends are the nuclear charge (number of protons in the nucleus), the number of electron shells, and the shielding effect of inner electrons.
2. How do periodic trends help in understanding the reactivity of elements?
Periodic trends help understand reactivity by providing insights into how easily an element loses or gains electrons. For example, elements with low ionization energies are more likely to lose electrons and be reactive, while those with high electron affinities are more likely to gain electrons and be reactive.
3. Can periodic trends be used to predict the properties of undiscovered elements?
Yes, periodic trends can be used to predict the properties of undiscovered elements. By extrapolating the trends observed for known elements, scientists can make educated guesses about the expected properties of new elements.
4. What are some exceptions to the periodic trends?
There are exceptions to the periodic trends, particularly for elements with half-filled or fully-filled electron shells. These exceptions arise from the stability associated with these electronic configurations.
5. Are periodic trends relevant only to chemistry?
While periodic trends are fundamental to chemistry, they also have applications in other fields like physics, materials science, and environmental science.
Tips for Mastering Periodic Trends
1. Visualize the Periodic Table: Familiarize yourself with the arrangement of elements on the periodic table and the location of key groups and periods.
2. Use Mnemonics: Create mnemonics to remember the trends. For example, "Across the period, ionization energy goes up, down the group, it goes down."
3. Practice with Examples: Work through practice problems and examples to solidify your understanding of how periodic trends apply to specific elements and compounds.
4. Connect Trends to Real-World Applications: Relate periodic trends to real-world phenomena like the reactivity of metals, the properties of semiconductors, and the behavior of pollutants.
5. Utilize Online Resources: Explore interactive periodic tables and online resources to visualize and explore the periodic trends in detail.
Conclusion
Chemistry periodic trends worksheet answers 2025 are fundamental concepts in chemistry that provide a framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of elements and compounds. By mastering these trends, students and professionals can gain a deeper understanding of the chemical world and its applications in various fields. Continuously exploring the periodic trends and their applications enhances the ability to predict and explain chemical phenomena, ultimately leading to a more comprehensive understanding of chemistry and its role in our world.
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)
/PeriodicTable-Trends-56a1310e5f9b58b7d0bcea8a-5c2d154e46e0fb0001f3647a.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Periodic Trends: A Comprehensive Guide to Chemical Properties. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
.PNG)